Exploring the Antioxidant and Genoprotective Potential of Salicornia ramosissima Incorporation in the Diet of the European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax)
- PMID: 38200822
- PMCID: PMC10778275
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14010093
Exploring the Antioxidant and Genoprotective Potential of Salicornia ramosissima Incorporation in the Diet of the European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax)
Abstract
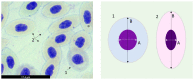
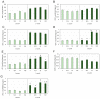
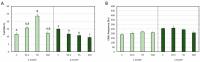
The identification of novel feed materials as a source of functional ingredients is a topical priority in the finfish aquaculture sector. Due to the agrotechnical practices associated and phytochemical profiling, halophytes emerge as a new source of feedstuff for aquafeeds, with the potential to boost productivity and environmental sustainability. Therefore, the present study aimed to assess the potential of Salicornia ramosissima incorporation (2.5, 5, and 10%), for 2 months, in the diet of juvenile European seabass, seeking antioxidant (in the liver, gills, and blood) and genoprotective (DNA and chromosomal integrity in blood) benefits. Halophyte inclusion showed no impairments on growth performance. Moreover, a tissue-specific antioxidant improvement was apparent, namely through the GSH-related defense subsystem, but revealing multiple and complex mechanisms. A genotoxic trigger (regarded as a pro-genoprotective mechanism) was identified in the first month of supplementation. A clear protection of DNA integrity was detected in the second month, for all the supplementation levels (and the most prominent melioration at 10%). Overall, these results pointed out a functionality of S. ramosissima-supplemented diets and a promising way to improve aquaculture practices, also unraveling a complementary novel, low-value raw material, and a path to its valorization.
Keywords: DNA integrity; fish feedstuff; functional feed; halophytes; sustainable aquaculture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dietary Salicornia ramosissima improves the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) inflammatory response against Photobacterium damselae piscicida.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1342144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342144. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38500885 Free PMC article.
-
Salicornia ramosissima Biomass as a Partial Replacement of Wheat Meal in Diets for Juvenile European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax).Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 14;14(4):614. doi: 10.3390/ani14040614. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396582 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary aquaculture by-product hydrolysates: impact on the transcriptomic response of the intestinal mucosa of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed low fish meal diets.BMC Genomics. 2018 May 24;19(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4780-0. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29793421 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Polyphenols in Salicornia ramosissima with Special Emphasis on Their Beneficial Effects on Brain Ischemia.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 3;15(3):793. doi: 10.3390/nu15030793. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36771496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediterranean Aquaculture in a Changing Climate: Temperature Effects on Pathogens and Diseases of Three Farmed Fish Species.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 16;10(9):1205. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091205. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34578236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of the UV Filter Octocrylene and Its Degradation Product Benzophenone on Pacific Oyster (Magallana gigas) Larvae: A Call for Reassessment of Environmental Hazards.Toxics. 2025 Feb 28;13(3):177. doi: 10.3390/toxics13030177. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40137504 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Salicornia ramosissima improves the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) inflammatory response against Photobacterium damselae piscicida.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1342144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342144. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38500885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turcios A.E., Cayenne A., Uellendahl H., Papenbrock J. Halophyte Plants and Their Residues as Feedstock for Biogas Production—Chances and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2021;11:2746. doi: 10.3390/app11062746. - DOI
-
- Giordano R., Saii Z., Fredsgaard M., Hulkko L.S.S., Poulsen T.B.G., Thomsen M.E., Henneberg N., Zucolotto S.M., Arendt-Nielsen L., Papenbrock J., et al. Pharmacological Insights into Halophyte Bioactive Extract Action on Anti-Inflammatory, Pain Relief and Antibiotics-Type Mechanisms. Molecules. 2021;26:3140. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113140. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hulkko L.S.S., Chaturvedi T., Thomsen M.H. Extraction and Quantification of Chlorophylls, Carotenoids, Phenolic Compounds, and Vitamins from Halophyte Biomasses. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:840. doi: 10.3390/app12020840. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

