A Comparison of the Intrarectal and Intramuscular Effects of a Dexmedetomidine, Ketamine and Midazolam Mixture on Tear Production in Cats: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38200876
- PMCID: PMC10778512
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14010145
A Comparison of the Intrarectal and Intramuscular Effects of a Dexmedetomidine, Ketamine and Midazolam Mixture on Tear Production in Cats: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
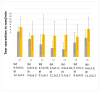
Cats are often easily stressed and uncooperative. The use of sedative agents in the feline species is widely used to perform even minor clinical and diagnostic procedures. The aim of this study is to assess the impact on tear film production of the intrarectal route (IR) administration of a mixture of dexmedetomidine, ketamine and midazolam in comparison with the intramuscular (IM) one. A group of twenty cats were involved in a randomized and blinded clinical trial. A clinical and ophthalmological examination was conducted on the cats. The IR group received dexmedetomidine 0.003 mg kg-1, ketamine 4 mg kg-1 and midazolam 0.4 mg kg-1; the IM group received dexmedetomidine 0.003 mg kg-1, ketamine 2 mg kg-1 and midazolam 0.2 mg kg-1. A Shirmer tear test I (STT- I) was conducted 1 h before sedation and 2', 10', 20', 30', 40', and 80' post drug administration. The reaction to STT-I administration was also evaluated. The IM group has a lower mean tear production than the IR group for all time points evaluated. Cats in the IM group showed less reaction to STT-I administration. This study may suggest that the effect of sedative agents administered by the IR route has a lower incidence on tear production than the IM one. The use of eye lubricant is recommended in any case.
Keywords: cats; dexmedetomidine; intramuscular route; intrarectal route; ketamine; midazolam; sedation; tear production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Certain Intrarectal versus Intramuscular Pharmacodynamic Effects of Ketamine, Dexmedetomidine and Midazolam in Cats.Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 23;9(10):520. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9100520. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36288133 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Comparison of Intramuscular Admixtures of Ketamine and Dexmedetomidine Versus Ketamine and Midazolam for Preoperative Sedation.Anesth Prog. 2021 Mar 1;68(1):3-9. doi: 10.2344/anpr-67-04-02. Anesth Prog. 2021. PMID: 33827122 Free PMC article.
-
Sedative and cardiorespiratory effects of dexmedetomidine and buprenorphine administered to cats via oral transmucosal or intramuscular routes.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2010 Sep;37(5):417-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2010.00555.x. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 20712608 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of two multimodal intramuscular anaesthetic protocols in uncooperative feline patients: effects on sedation and echocardiographic measurements.J Feline Med Surg. 2023 Feb;25(2):1098612X231153069. doi: 10.1177/1098612X231153069. J Feline Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36820491 Free PMC article.
-
Anesthetic effects of the ketamine and midazolam association by intranasal or intramuscular route in domestic chickens: prospective, blinded, randomized and crossover study.Braz J Vet Med. 2024 Jul 4;46:e005953. doi: 10.29374/2527-2179.bjvm005923. eCollection 2024. Braz J Vet Med. 2024. PMID: 39036333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

