Electro-Acupuncture Effects Measured by Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging-A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials
- PMID: 38200908
- PMCID: PMC10778902
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12010002
Electro-Acupuncture Effects Measured by Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging-A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
Introduction: Electro-acupuncture, an innovative adaptation of traditional acupuncture, combines electrical stimulation with acupuncture needles to enhance therapeutic effects. While acupuncture is widely used, its biological mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Recent research has explored the neurophysiological aspects of acupuncture, particularly through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to investigate its effects on brain activity.
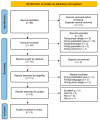
Methods: In this systematic review, we conducted an extensive search for randomized clinical trials examining electro-acupuncture effects measured by fMRI. We employed strict eligibility criteria, quality assessment, and data extraction.
Results: Five studies met our inclusion criteria and were analyzed. The selected studies investigated electro-acupuncture in various medical conditions, including carpal tunnel syndrome, fibromyalgia, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and obesity. Notably, electro-acupuncture was found to modulate brain activity and connectivity in regions associated with pain perception, emotional regulation, and cognitive processing. These findings align with the holistic approach of traditional Chinese medicine, emphasizing the interconnectedness of body and mind.
Discussion: In carpal tunnel syndrome, electro-acupuncture at both local and distal sites showed neurophysiological improvements, suggesting distinct neuroplasticity mechanisms. In fibromyalgia, somatosensory electro-acupuncture correlated with reduced pain severity, enhanced brain connectivity, and increased gamma-aminobutyric acid levels. For Crohn's disease, electro-acupuncture influenced the homeostatic afferent processing network, potentially mitigating gut inflammation. Electro-acupuncture for irritable bowel syndrome led to decreased activity in the anterior cingulate cortex, offering pain relief, while electro-acupuncture for obesity impacted brain regions associated with dietary inhibition and emotional regulation.
Conclusion: This systematic review provides evidence that electro-acupuncture can positively impact a range of medical conditions, possibly by modulating brain activity and connectivity. While the quality of the reviewed studies is generally good, further research with larger sample sizes and longer-term assessments is needed to better understand the mechanisms and optimize electro-acupuncture protocols for specific health conditions. The limited number of studies in this review emphasizes the need for broader investigations in this promising field. The research protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023465866).
Keywords: complementary therapies; electro-acupuncture; fMRI; integrative medicine; neurosciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rewiring the primary somatosensory cortex in carpal tunnel syndrome with acupuncture.Brain. 2017 Apr 1;140(4):914-927. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx015. Brain. 2017. PMID: 28334999 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Electro-Acupuncture and Moxibustion on Brain Connectivity in Patients with Crohn's Disease: A Resting-State fMRI Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Nov 17;11:559. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00559. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29204113 Free PMC article.
-
S1 Brain Connectivity in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Underlies Median Nerve and Functional Improvement Following Electro-Acupuncture.Front Neurol. 2021 Oct 27;12:754670. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.754670. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34777225 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of acupuncture on brain regions modulation of mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Sep 23;14:914049. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.914049. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36212046 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of electroacupuncture combined with rehabilitation techniques on shoulder function in patients with rotator cuff injuries.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jul 26;12(21):4582-4589. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4582. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39070812 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Effect of Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation on Postural Control: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Physiother Res Int. 2025 Oct;30(4):e70099. doi: 10.1002/pri.70099. Physiother Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40839635 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Current Research in Drug-Free Cancer Therapies.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;12(4):341. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12040341. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nakatani Y. Skin electric resistance and Ryodoraku. J. Auton. Nerve. 1956;6:52.
-
- Burns L. Viscero-somatic and somato-visceral spinal reflexes. 1907. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2000;100:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Bath M., Owens J. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Physiology, viscerosomatic reflexes. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous