Simple Purification and Antimicrobial Properties of Bacteriocin-like Inhibitory Substance from Bacillus Species for the Biopreservation of Cheese
- PMID: 38201038
- PMCID: PMC10778428
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13010010
Simple Purification and Antimicrobial Properties of Bacteriocin-like Inhibitory Substance from Bacillus Species for the Biopreservation of Cheese
Abstract
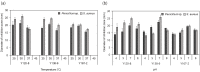
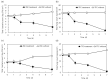
Bacteriocins may be used as natural preservatives and antibiotic substitutes in various foods. However, the multistep purification process of bacteriocins results in high production costs, which is an obstacle to their commercial use and consumer accessibility. In this study, a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance (BLIS) from Bacillus spp. isolated from Korean fermented foods was partially purified using the aqueous two-phase system (ATPS). The maximum activity of the BLIS was achieved for ATPS composed of PEG 1000 (15% [w/w])/ammonium sulfate (20% [w/w])/sodium chloride (2% [w/w]), which caused BLIS activity to increase by 3 times with a 99% recovery rate. In particular, B. amyloliquefaciens Y138-6 BLIS exhibited broad antibacterial activity, high resistance to acid-base stress, and excellent thermal stability. This antibacterial substance inhibited the growth of aerobic bacteria and fungi on the walls of cheese and ripening rooms. These antibacterial properties have been shown to increase food safety and have the potential for use as biopreservatives. Moreover, considering that the execution of the ATPS requires only salts and PEG, it is a simple, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective process and may have industrial applications in the recovery of BLIS from fermentation broth.
Keywords: Bacillus; aqueous two-phase system; bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Milioni C., Martínez B., Degl’Innocenti S., Turchi B., Fratini F., Cerri D., Fischetti R. A novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum LpU4 as a valuable candidate for biopreservation in artisanal raw milk cheese. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015;95:479–494. doi: 10.1007/s13594-015-0230-9. - DOI
-
- Beresford T., Williams A. The Microbiology of Cheese Ripening. In: Fox P.F., McSweeney P.L., Cogan T.M., Guinee T.P., editors. Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology. 3rd ed. Volume 1. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2004. pp. 287–318.
-
- Ledenbach L.H., Marshall R.T. Compendium of the Microbiological Spoilage of Foods and Beverages. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2009. Microbiological Spoilage of Dairy Products; pp. 41–67.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

