Combining AI Tools with Non-Destructive Technologies for Crop-Based Food Safety: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38201039
- PMCID: PMC10777928
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13010011
Combining AI Tools with Non-Destructive Technologies for Crop-Based Food Safety: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
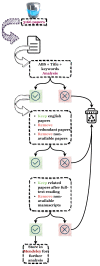
On a global scale, food safety and security aspects entail consideration throughout the farm-to-fork continuum, considering food's supply chain. Generally, the agrifood system is a multiplex network of interconnected features and processes, with a hard predictive rate, where maintaining the food's safety is an indispensable element and is part of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It has led the scientific community to develop advanced applied analytical methods, such as machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques applied for assessing foodborne diseases. The main objective of this paper is to contribute to the development of the consensus version of ongoing research about the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools in the domain of food-crop safety from an analytical point of view. Writing a comprehensive review for a more specific topic can also be challenging, especially when searching within the literature. To our knowledge, this review is the first to address this issue. This work consisted of conducting a unique and exhaustive study of the literature, using our TriScope Keywords-based Synthesis methodology. All available literature related to our topic was investigated according to our criteria of inclusion and exclusion. The final count of data papers was subject to deep reading and analysis to extract the necessary information to answer our research questions. Although many studies have been conducted, limited attention has been paid to outlining the applications of AI tools combined with analytical strategies for crop-based food safety specifically.
Keywords: chemometrics; food contaminants; food processes; machine learning; spectroscopy; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


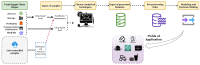
Similar articles
-
AI-Powered Innovations in Food Safety from Farm to Fork.Foods. 2025 Jun 2;14(11):1973. doi: 10.3390/foods14111973. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Boosting precision crop protection towards agriculture 5.0 via machine learning and emerging technologies: A contextual review.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 22;14:1143326. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1143326. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37056493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of AI - reshaping the future of food safety, agriculture and food security - a critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 7:1-45. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2430749. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39644464 Review.
-
Advanced detection tools in food fraud: A systematic review for holistic and rational detection method based on research and patents.Food Chem. 2024 Jul 15;446:138893. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138893. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38432137
Cited by
-
Intelligent Rapid Detection Techniques for Low-Content Components in Fruits and Vegetables: A Comprehensive Review.Foods. 2024 Apr 6;13(7):1116. doi: 10.3390/foods13071116. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38611420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Image Computing in Non-Destructive Detection of Chinese Cuisine.Foods. 2025 Jul 16;14(14):2488. doi: 10.3390/foods14142488. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-field microwave sensing technology enhanced with machine learning for the non-destructive evaluation of packaged food and beverage products.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 11;14(1):13413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62287-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38862556 Free PMC article.
-
AI-Powered Innovations in Food Safety from Farm to Fork.Foods. 2025 Jun 2;14(11):1973. doi: 10.3390/foods14111973. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NIR sensors combined with chemometric algorithms in intelligent quality evaluation of sweetpotato roots from 'Farm' to 'Table': Progresses, challenges, trends, and prospects.Food Chem X. 2024 May 7;22:101449. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101449. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38784692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garcia S.N., Osburn B.I., Jay-Russell M.T. One health for food safety, food security, and sustainable food production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020;4:1. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.00001. - DOI
-
- Matthews P.J., Ghanem M.E. Perception gaps that may explain the status of taro (Colocasia esculenta) as an “orphan crop”. Plants People Planet. 2021;3:99–112. doi: 10.1002/ppp3.10155. - DOI
-
- Neufeld L.M., Hendriks S., Hugas M. A Paper from the Scientific Group of the UN Food Systems Summit. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. Healthy Diet: A Definition for the United Nations Food Systems Summit 2021. - PubMed
-
- FAO . Thinking about the Future of Food Safety—A Foresight Report. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2022. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

