Impact of Nanoclays Addition on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Flour Film Properties
- PMID: 38201103
- PMCID: PMC10778780
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13010075
Impact of Nanoclays Addition on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Flour Film Properties
Abstract
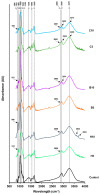
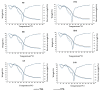
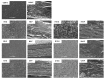
Chickpea flour is an affordable natural blend of starch, proteins, and lipids, which can create films with suitable properties as an eco-friendly packaging material. Nanoclays' incorporation into natural biopolymers enhances the barrier properties of the resulting nanocomposites, so they could improve the properties of flour films. The objective of this work was to assess the influence of three types of nanoclays (halloysite, bentonite, and Cloisite 20A) at two concentrations on the characteristics of chickpea flour films. In general terms, when the lowest dose (5%) was added, no or very slight significant differences with the control were observed in most parameters, except for thermal stability and opacity, which increased, and solubility, which decreased. At the highest concentration (10%), films containing any of the nanoclays demonstrated greater thermal stability, opacity, and rigidity while being less soluble than those without nanofillers. Bentonite exhibited superior film structure distribution compared to other nanoclays. At the highest concentration, it had the most significant impact on modifying the properties of chickpea flour films, increasing their tensile and puncture strengths while decreasing elasticity and water vapor permeability. The incorporation of nanoclays into chickpea flour films could be a useful technique to enhance their properties.
Keywords: Cloisite 20A; bentonite; biopolymer films; halloysite; mechanical properties; microstructure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Flour Films: Effects of pH and Plasticizer Concentration.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 12;20(5):1246. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051246. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30871074 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the properties of starch/chitosan films with the incorporation of various nanoclays for use in food packaging.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;298:140054. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140054. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39828182
-
Effect of Clay Nanofillers on the Mechanical and Water Vapor Permeability Properties of Xylan-Alginate Films.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Oct 4;12(10):2279. doi: 10.3390/polym12102279. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33020377 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoclays-containing bio-based packaging materials: properties, applications, safety, and regulatory issues.J Nanostructure Chem. 2023 Feb 2:1-23. doi: 10.1007/s40097-023-00525-5. Online ahead of print. J Nanostructure Chem. 2023. PMID: 36747507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Nanofillers on the Functional Properties of Biopolymer-based Films: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Apr 12;11(4):675. doi: 10.3390/polym11040675. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31013855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jarfarzadeh S., Forough M., Amjadi S., Kouzegaran V.J., Almasi H., Gravand F., Zargar M. Plant protein-based nanocomposite films: A review on the used nanomaterials, characteristics, and food packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022;62:1–28. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2070721. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kocakulak S., Sumnu G., Sahin S. Chickpea flour-based biofilms containing gallic acid to be used as active edible films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019;2019:47704. doi: 10.1002/app.47704. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

