Optimization and In Vitro Digestion of a Guava (Psidium guajava), Mamey (Pouteria sapota) and Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) Functional Beverage
- PMID: 38201170
- PMCID: PMC10778707
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13010142
Optimization and In Vitro Digestion of a Guava (Psidium guajava), Mamey (Pouteria sapota) and Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) Functional Beverage
Abstract
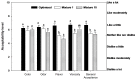
Guava and mamey are phenolic- and carotenoid-rich fruits with potential health benefits, but are minimally used as ingredients in functional beverages. The objectives of the present work are to optimize the content of guava and mamey pulps and a stevia solution in the formulation of a functional beverage with high content of bioactive compounds and sensory acceptability using a mixture design analysis, and to analyze its composition after in vitro digestion. The optimized formulation (17.77 and 19.23 g of guava and mamey pulps, respectively; 1% stevia solution) yielded a beverage with 418.21 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/100 mL and 0.20 mg β-carotene/100 mL, and an antioxidant capacity of 213.58, 78.90 and 234.03 mg Trolox equivalents (TE)/100 mL using three methodologies. The mathematical model developed was significant (p < 0.05), according to R2 values between 0.70 and 0.75. α- and β-carotene were quantified during the oral phase of in vitro digestion. Gallic, p-coumaric, ferulic and chlorogenic acids were also identified. The beverage had a general acceptability of 6.72. We conclude that the mathematical model developed was a good predictor of the experimental data and that the optimized beverage contained high bioactive concentrations (phenolics and carotenoids) and was well-accepted by potential consumers.
Keywords: D-optimal design; carotenoids; functional beverage; in vitro digestion; mixture design; phenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ardid-Ruiz A., Harazin A., Barna L., Walter F.R., Bladé C., Suárez M., Deli M.A., Aragonès G. The Effects of Vitis Vinifera L. Phenolic Compounds on a Blood-Brain Barrier Culture Model: Expression of Leptin Receptors and Protection against Cytokine-Induced Damage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020;247:112253. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112253. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaput J.P., Tremblay M.S., Katzmarzyk P.T., Fogelholm M., Hu G., Maher C., Maia J., Olds T., Onywera V., Sarmiento O.L., et al. Sleep Patterns and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption among Children from around the World. Public Health Nutr. 2018;21:2385–2393. doi: 10.1017/S1368980018000976. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources