A Comprehensive Review of the Potential Role of Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Predictive Biomarker in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38201207
- PMCID: PMC10778087
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13010003
A Comprehensive Review of the Potential Role of Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Predictive Biomarker in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
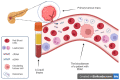
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the most lethal malignant diseases, with a mortality rate being close to incidence. Due to its heterogeneity and plasticity, as well as the lack of distinct symptoms in the early phases, it is very often diagnosed at an advanced stage, resulting in poor prognosis. Traditional tissue biopsies remain the gold standard for making a diagnosis, but have an obvious disadvantage in their inapplicability for frequent sampling. Blood-based biopsies represent a non-invasive method which potentially offers easy and repeated sampling, leading to the early detection and real-time monitoring of the disease and hopefully an accurate prognosis. Given the urgent need for a reliable biomarker that can estimate a patient's condition and response to an assigned treatment, blood-based biopsies are emerging as a potential new tool for improving patients' survival and surveillance. In this article, we discuss the current advances and challenges in using liquid biopsies for pancreatic cancer, focusing on circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA), extracellular vesicles (EVs), and circulating tumour cells (CTCs), and compare the performance and reliability of different biomarkers and combinations of biomarkers.
Keywords: liquid biopsy; pancreatic cancer; tumoural heterogeneity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ducreux M., Cuhna A.S., Caramella C., Hollebecque A., Burtin P., Goéré D., Seufferlein T., Haustermans K., Van Laethem J.L., Conroy T., et al. Cancer of the Pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:v56–v68. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv295. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical