Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics
- PMID: 38201218
- PMCID: PMC10778189
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13010014
Brain Region Differences in α1- and α5-Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor Proteomes Revealed with Affinity Purification and Blue Native PAGE Proteomics
Abstract
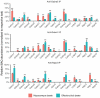
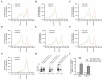
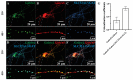
GABAA receptors are the major inhibitory receptors in the brain. They are hetero-pentamers with a composition of predominantly two α, two β, and one γ or δ subunit. Of the six α subunit genes, the α5 subunit displays a limited spatial expression pattern and is known to mediate both phasic and tonic inhibition. In this study, using immunoaffinity-based proteomics, we identified the α5 subunit containing receptor complexes in the hippocampus and olfactory bulb. The α1-α5 interaction was identified in both brain regions, albeit with significantly different stoichiometries. In line with this, reverse IPs using anti-α1 antibodies showed the α5-α1 co-occurrence and validated the quantitative difference. In addition, we showed that the association of Neuroligin 2 with α1-containing receptors was much higher in the olfactory bulb than in the hippocampus, which was confirmed using blue native gel electrophoresis and quantitative mass spectrometry. Finally, immunocytochemical staining revealed a co-localization of α1 and α5 subunits in the post-synaptic puncta in the hippocampus.
Keywords: GABAA receptor; brain; immunocytochemistry; immunoprecipitation; proteomics; synapse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

