Pathophysiological Effects of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Encephalitides
- PMID: 38201219
- PMCID: PMC10778077
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13010015
Pathophysiological Effects of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Encephalitides
Abstract
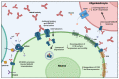
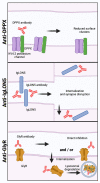
The heterogeneity of autoantibody targets in autoimmune encephalitides presents a challenge for understanding cellular and humoral pathophysiology, and the development of new treatment strategies. Thus, current treatment aims at autoantibody removal and immunosuppression, and is primarily based on data generated from other autoimmune neurological diseases and expert consensus. There are many subtypes of autoimmune encephalitides, which now entails both diseases with autoantibodies targeting extracellular antigens and classical paraneoplastic syndromes with autoantibodies targeting intracellular antigens. Here, we review the current knowledge of molecular and cellular effects of autoantibodies associated with autoimmune encephalitis, and evaluate the evidence behind the proposed pathophysiological mechanisms of autoantibodies in autoimmune encephalitis.
Keywords: autoimmune encephalitides; molecular mechanisms; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Koneczny I., Tzartos J., Mane-Damas M., Yilmaz V., Huijbers M.G., Lazaridis K., Hoftberger R., Tuzun E., Martinez-Martinez P., Tzartos S., et al. IgG4 Autoantibodies in Organ-Specific Autoimmunopathies: Reviewing Class Switching, Antibody-Producing Cells, and Specific Immunotherapies. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:834342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.834342. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

