Understanding Bartonella-Associated Infective Endocarditis: Examining Heart Valve and Vegetation Appearance and the Role of Neutrophilic Leukocytes
- PMID: 38201247
- PMCID: PMC10778237
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13010043
Understanding Bartonella-Associated Infective Endocarditis: Examining Heart Valve and Vegetation Appearance and the Role of Neutrophilic Leukocytes
Abstract
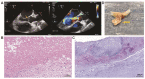
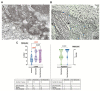
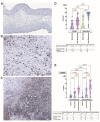
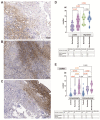
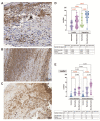
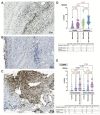
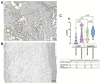
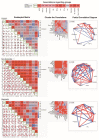
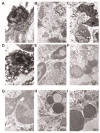
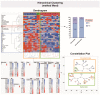
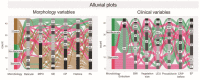
The endocardium and cardiac valves undergo severe impact during infective endocarditis (IE), and the formation of vegetation places IE patients at a heightened risk of embolic complications and mortality. The relevant literature indicates that 50% of IE cases exhibit structurally normal cardiac valves, with no preceding history of heart valve disease. Gram-positive cocci emerge as the predominant causative microorganisms in IE, while Gram-negative Bartonella spp., persisting in the endothelium, follow pathogenic pathways distinct from those of typical IE-causing agents. Employing clinical as well as advanced microbiological and molecular assays facilitated the identification of causative pathogens, and various morphological methods were applied to evaluate heart valve damage, shedding light on the role of neutrophilic leukocytes in host defense. In this research, the immunohistochemical analysis of neutrophilic leukocyte activation markers such as myeloperoxidase, neutrophil elastase, calprotectin, and histone H3, was performed. A distinct difference in the expression patterns of these markers was observed when comparing Bartonella spp.-caused and non-Bartonella spp.-caused IE. The markers exhibited significantly higher expression in non-Bartonella spp.-caused IE compared to Bartonella spp.-caused IE, and they were more prevalent in vegetation than in the valvular leaflets. Notably, the expression of these markers in all IE cases significantly differed from that in control samples. Furthermore, we advocated the use of 16S rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing on excised heart valves as an effective diagnostic tool for IE, particularly in cases where blood cultures yielded negative results. The compelling results achieved in this study regarding the enigmatic nature of Bartonella spp. IE's pathophysiology contribute significantly to our understanding of the peculiarities of inflammation and immune responses.
Keywords: Bartonella spp.; cardiac valves; infective endocarditis; neutrophil extracellular traps; neutrophils; vegetation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abiotrophia spp. and Granulicatella spp. Infective Endocarditis: A Contemporary Perspective.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2022 Aug 18;14(3):23. doi: 10.31083/j.fbe1403023. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2022. PMID: 36137991
-
Clinical Significance of a 16S-rDNA Analysis of Heart Valves in Patients with Infective Endocarditis: a Retrospective Study.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0113623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01136-23. Epub 2023 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37195215 Free PMC article.
-
16S rRNA Gene PCR/Sequencing of Heart Valves for Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Routine Clinical Practice.J Clin Microbiol. 2023 Aug 23;61(8):e0034123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.00341-23. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37436146 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological differences between Bartonella and other bacterial endocarditis-related glomerulonephritis - our experience and a pooled analysis.Front Nephrol. 2024 Jan 15;3:1322741. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2023.1322741. eCollection 2023. Front Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38288381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infective endocarditis caused by Streptococcus sinensis diagnosed with next-generation sequencing: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 27;25(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10837-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40148753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Diversity in Native Heart Valves in Infective Endocarditis.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 20;13(1):245. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010245. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857828 Free PMC article.
-
The cruciality of increasing index of suspicion for atypical Bartonella henselae in pediatric patients: A case series.IDCases. 2025 Mar 5;40:e02192. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2025.e02192. eCollection 2025. IDCases. 2025. PMID: 40129759 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

