The Emerging Role of SIRT7 in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 38201252
- PMCID: PMC10778536
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13010048
The Emerging Role of SIRT7 in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
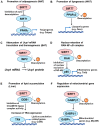
Sirtuins (SIRT1-7 in mammals) are a family of NAD+-dependent lysine deacetylases and deacylases that regulate diverse biological processes, including metabolism, stress responses, and aging. SIRT7 is the least well-studied member of the sirtuins, but accumulating evidence has shown that SIRT7 plays critical roles in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism by modulating many target proteins in white adipose tissue, brown adipose tissue, and liver tissue. This review focuses on the emerging roles of SIRT7 in glucose and lipid metabolism in comparison with SIRT1 and SIRT6. We also discuss the possible implications of SIRT7 inhibition in the treatment of metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Keywords: SIRT1; SIRT6; SIRT7; diabetes; obesity; sirtuin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Haigis M.C., Mostoslavsky R., Haigis K.M., Fahie K., Christodoulou D.C., Murphy A.J.J., Valenzuela D.M., Yancopoulos G.D., Karow M., Blander G., et al. SIRT4 Inhibits Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Opposes the Effects of Calorie Restriction in Pancreatic β Cells. Cell. 2006;126:941–954. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.057. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

