Neuronal Autophagy: Regulations and Implications in Health and Disease
- PMID: 38201307
- PMCID: PMC10778363
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13010103
Neuronal Autophagy: Regulations and Implications in Health and Disease
Abstract
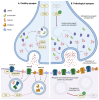
Autophagy is a major degradative pathway that plays a key role in sustaining cell homeostasis, integrity, and physiological functions. Macroautophagy, which ensures the clearance of cytoplasmic components engulfed in a double-membrane autophagosome that fuses with lysosomes, is orchestrated by a complex cascade of events. Autophagy has a particularly strong impact on the nervous system, and mutations in core components cause numerous neurological diseases. We first review the regulation of autophagy, from autophagosome biogenesis to lysosomal degradation and associated neurodevelopmental/neurodegenerative disorders. We then describe how this process is specifically regulated in the axon and in the somatodendritic compartment and how it is altered in diseases. In particular, we present the neuronal specificities of autophagy, with the spatial control of autophagosome biogenesis, the close relationship of maturation with axonal transport, and the regulation by synaptic activity. Finally, we discuss the physiological functions of autophagy in the nervous system, during development and in adulthood.
Keywords: autophagy; compartmentalisation; neurodegeneration; neurodevelopment; regulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular regulation of autophagosome formation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Feb 28;50(1):55-69. doi: 10.1042/BST20210819. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35076688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal autophagy and the implications in neurodegenerative diseases.Neurobiol Dis. 2022 Jan;162:105582. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105582. Epub 2021 Dec 7. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 34890791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Axonal autophagy: Mini-review for autophagy in the CNS.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Apr 1;697:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.03.025. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 29548988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy in mammalian neurodevelopment and implications for childhood neurological disorders.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Apr 1;697:29-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.04.017. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 29665429 Review.
-
The secret life of degradative lysosomes in axons: delivery from the soma, enzymatic activity, and local autophagic clearance.Autophagy. 2020 Jan;16(1):167-168. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1669869. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31533518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal opioid exposure alters pain perception and increases long-term health risks in infants with neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 17;6:1497801. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2025.1497801. eCollection 2025. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40313396 Free PMC article.
-
Caloric restriction mimetics improve gut microbiota: a promising neurotherapeutics approach for managing age-related neurodegenerative disorders.Biogerontology. 2024 Nov;25(6):899-922. doi: 10.1007/s10522-024-10128-4. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 39177917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of autophagy in the pathogenesis and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD).Autophagy Rep. 2025 Mar 20;4(1):2474796. doi: 10.1080/27694127.2025.2474796. eCollection 2025. Autophagy Rep. 2025. PMID: 40395983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for E3 ubiquitin ligases in neural development and disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 27;13:1557653. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1557653. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40496139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Human Genetic and Cellular Analysis of the Pathophysiological Roles of AnxA2 in Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;13(10):1274. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101274. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456526 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

