Navigation and Robotics in Interventional Oncology: Current Status and Future Roadmap
- PMID: 38201407
- PMCID: PMC10795729
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14010098
Navigation and Robotics in Interventional Oncology: Current Status and Future Roadmap
Abstract
Interventional oncology (IO) is the field of Interventional Radiology that provides minimally invasive procedures under imaging guidance for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors. Sophisticated devices can be utilized to increase standardization, accuracy, outcomes, and "repeatability" in performing percutaneous Interventional Oncology techniques. These technologies can reduce variability, reduce human error, and outperform human hand-to-eye coordination and spatial relations, thus potentially normalizing an otherwise broad diversity of IO techniques, impacting simulation, training, navigation, outcomes, and performance, as well as verification of desired minimum ablation margin or other measures of successful procedures. Stereotactic navigation and robotic systems may yield specific advantages, such as the potential to reduce procedure duration and ionizing radiation exposure during the procedure and, at the same time, increase accuracy. Enhanced accuracy, in turn, is linked to improved outcomes in many clinical scenarios. The present review focuses on the current role of percutaneous navigation systems and robotics in diagnostic and therapeutic Interventional Oncology procedures. The currently available alternatives are presented, including their potential impact on clinical practice as reflected in the peer-reviewed medical literature. A review of such data may inform wiser investment of time and resources toward the most impactful IR/IO applications of robotics and navigation to both standardize and address unmet clinical needs.
Keywords: ablation; biopsy; navigation; robotics.
Conflict of interest statement
Reto Bale is a consultant for Interventional Systems.
Figures
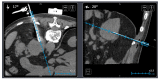
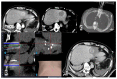
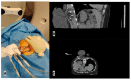

Similar articles
-
Image-Guided Robotics for Standardized and Automated Biopsy and Ablation.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2021 Nov 24;38(5):565-575. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1739164. eCollection 2021 Dec. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34853503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robotics in Interventional Radiology: Review of Current and Future Applications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231152084. doi: 10.1177/15330338231152084. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37113061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Planning and guidance: New tools to enhance the human skills in interventional oncology.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2017 Sep;98(9):583-588. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28818346 Review.
-
Navigational Tools for Interventional Radiology and Interventional Oncology Applications.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2015 Dec;32(4):416-27. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1564705. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26622105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the clinical benefit of an electromagnetic navigation system for CT-guided interventional radiology procedures in the thoraco-abdominal region compared with conventional CT guidance (CTNAV II): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Jul 6;18(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2049-6. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28683837 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Surgery or Percutaneous Ablation for Liver Tumors? The Key Points Are: When, Where, and How Large.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;17(8):1344. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081344. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282520 Free PMC article.
-
A review of image guidance and localization methods for liver puncture robots.J Robot Surg. 2025 Apr 17;19(1):163. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02328-y. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40244465 Review.
-
Stereotactic Percutaneous Electrochemotherapy as a New Minimal Invasive Treatment Modality for Primary and Secondary Liver Malignancies.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 17;12(12):2870. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122870. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767776 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations in Image-Guided Procedures: Unraveling Robot-Assisted Non-Hepatic Percutaneous Ablation.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2024 Jul 10;41(2):113-120. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1786724. eCollection 2024 Apr. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38993597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robot-Assisted 2D Fluoroscopic Needle Placement-A Phantom Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;14(16):1723. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161723. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lanza C., Carriero S., Buijs E.F.M., Mortellaro S., Pizzi C., Sciacqua L.V., Biondetti P., Angileri S.A., Ianniello A.A., Ierardi A.M., et al. Robotics in Interventional Radiology: Review of Current and Future Applications. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023;22:15330338231152084. doi: 10.1177/15330338231152084. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

