A Sequent of Gram-Negative Co-Infectome-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Are Potentially Subtle Aggravators Associated to the SARS-CoV-2 Evolution of Virulence
- PMID: 38201429
- PMCID: PMC10802668
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14010120
A Sequent of Gram-Negative Co-Infectome-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Are Potentially Subtle Aggravators Associated to the SARS-CoV-2 Evolution of Virulence
Abstract
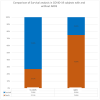
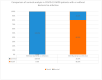
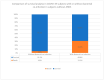
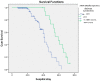
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is one of the major problems in COVID-19 that is not well understood. ARDS is usually complicated by co-infections in hospitals. Although ARDS is inherited by Europeans and Africans, this is not clear for those from the Middle East. There are severe limitations in correlations made between COVID-19, ARDS, co-infectome, and patient demographics. We investigated 298 patients for associations of ARDS, coinfections, and patient demographics on COVID-19 patients' outcomes. Of the 149 patients examined for ARDS during COVID-19, 16 had an incidence with a higher case fatality rate (CFR) of 75.0% compared to those without ARDS (27.0%) (p value = 0.0001). The co-infectome association showed a CFR of 31.3% in co-infected patients; meanwhile, only 4.8% of those without co-infections (p value = 0.01) died. The major bacteria were Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli, either alone or in a mixed infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of COVID-19 patients with and without ARDS revealed a significant difference in the survival time of patients with ARDS (58.8 +/- 2.7 days) and without ARDS (41.9 +/- 1.8 days) (p value = 0.0002). These findings prove that increased hospital time was risky for co-infectome-induced SDRS later on. This also explained that while empiric therapy and lethal ventilations delayed the mortality in 75% of patients, they potentially did not help those without co-infection or ARDS who stayed for shorter times. In addition, the age of patients (n = 298) was significantly associated with ARDS (72.9 +/- 8.9) compared to those without it (56.2 +/- 15.1) and was irrespective of gender. However, there were no significant differences neither in the age of admitted patients before COVID-19 (58.5 +/- 15.3) and during COVID-19 (57.2 +/- 15.5) nor in the gender and COVID-19 fatality (p value 0.546). Thus, Gram-negative co-infectome potentially induced fatal ARDS, aggravating the COVID-19 outcome. These findings are important for the specific differential diagnosis of patients with and without ARDS and co-infections. Future vertical investigations on mechanisms of Gram-negative-induced ARDS are imperative since hypervirulent strains are rapidly circulating. This study was limited as it was a single-center study confined to Ha'il hospitals; a large-scale investigation in major national hospitals would gain more insights.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19 fatality; co-evolution of virulence; co-infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gajic O., Dabbagh O., Park P.K., Adesanya A., Chang S.Y., Hou P., Anderson H., Hoth J.J., Mikkelsen M.E., Gentile N.T., et al. Early Identification of Patients at Risk of Acute Lung Injury: Evaluation of Lung Injury Prediction Score in a Multicenter Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011;183:462–470. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201004-0549OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

