Sunitinib Treatment of VHL C162F Cells Slows Down Proliferation and Healing Ability via Downregulation of ZHX2 and Confers a Mesenchymal Phenotype
- PMID: 38201462
- PMCID: PMC10778532
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16010034
Sunitinib Treatment of VHL C162F Cells Slows Down Proliferation and Healing Ability via Downregulation of ZHX2 and Confers a Mesenchymal Phenotype
Abstract
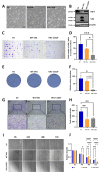
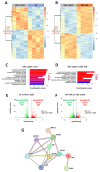
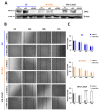
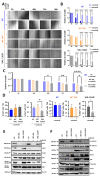
von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease, due to mutations of the tumor suppressor VHL gene, is a rare hereditary syndrome with a high risk of developing clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). We asked whether the VHL-C162F mutation interferes with proliferation, migration, healing and forming colony ability by using wild-type VHL (WT VHL) and VHL-C162F reconstituted cells. We then analyzed the in vitro impact of the sunitinib treatment on VHL-C162F cells. We showed that VHL-C162F mutations have no impact on cell morphology, colony formation and migration ability but confer a significant higher healing ability than in WT VHL cells. RNA sequencing analysis revealed that VHL-C162F mutation upregulates genes involved in hypoxia and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathways by comparison with VHL WT cells. We next showed a decrease in healing ability in VHL-C162F cells depleting on ZHX2, an oncogenic driver of ccRCC, highlighting the potential involvement of ZHX2 in aggressiveness of the VHL-C162F cells. Moreover, we found that sunitinib treatment inhibits ZHX2 expression and induces a reduced proliferation correlating with downregulation of P-ERK. Sunitinib treatment also conferred a more mesenchymal profile to VHL-C162F cells with significant downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of N-cadherin, Slug and AXL. Sunitinib therapy may therefore promote disease progression in VHL-C162F patients.
Keywords: VHL-C162F mutation; ZHX2; ccRCCs; epithelial mesenchymal transition; hypoxia-related genes; sunitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ZHX2 drives cell growth and migration via activating MEK/ERK signal and induces Sunitinib resistance by regulating the autophagy in clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2020 May 7;11(5):337. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2541-x. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32382017 Free PMC article.
-
The Most Common VHL Point Mutation R167Q in Hereditary VHL Disease Interferes with Cell Plasticity Regulation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 2;13(15):3897. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153897. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359798 Free PMC article.
-
VHL substrate transcription factor ZHX2 as an oncogenic driver in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Science. 2018 Jul 20;361(6399):290-295. doi: 10.1126/science.aap8411. Science. 2018. PMID: 30026228 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential pathogenesis of metastatic VHL mutant clear cell renal cell carcinoma: putting it together with a translational perspective.Ann Oncol. 2016 Sep;27(9):1685-95. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw241. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27329246 Review.
-
Downstream Targets of VHL/HIF-α Signaling in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma Progression: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 19;15(4):1316. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041316. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eleven inflammation-related genes risk signature model predicts prognosis of patients with breast cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 31;13(7):3652-3667. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-215. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39145071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tabata M., Sato Y., Kogure Y., McClure M.B., Oshikawa-Kumade Y., Saito Y., Shingaki S., Ito Y., Yuasa M., Koya J., et al. Inter- and intra-tumor heterogeneity of genetic and immune profiles in inherited renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2023;42:112736. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112736. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

