Exploiting the DNA Damage Response for Prostate Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 38201511
- PMCID: PMC10777950
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16010083
Exploiting the DNA Damage Response for Prostate Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Prostate cancers that progress despite androgen deprivation develop into castration-resistant prostate cancer, a fatal disease with few treatment options. In this review, we discuss the current understanding of prostate cancer subtypes and alterations in the DNA damage response (DDR) that can predispose to the development of prostate cancer and affect its progression. We identify barriers to conventional treatments, such as radiotherapy, and discuss the development of new therapies, many of which target the DDR or take advantage of recurring genetic alterations in the DDR. We place this in the context of advances in understanding the genetic variation and immune landscape of CRPC that could help guide their use in future treatment strategies. Finally, we discuss several new and emerging agents that may advance the treatment of lethal disease, highlighting selected clinical trials.
Keywords: ATM; ATR; DNA damage response; DNA-PK; PARP; androgen; hypoxia; immunotherapy; prostate cancer; radiopharmaceutical therapy; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
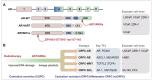
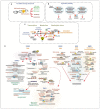
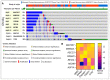
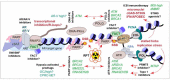
References
-
- Mohler J.L., Antonarakis E.S., Armstrong A.J., D’Amico A.V., Davis B.J., Dorff T., Eastham J.A., Enke C.A., Farrington T.A., Higano C.S., et al. Prostate Cancer, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019;17:479–505. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lavaud P., Dumont C., Thibault C., Albiges L., Baciarello G., Colomba E., Flippot R., Fuerea A., Loriot Y., Fizazi K. Next-Generation Androgen Receptor Inhibitors in Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020;12:1758835920978134. doi: 10.1177/1758835920978134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

