PI3Kδ Inhibition Potentiates Glucocorticoids in B-lymphoblastic Leukemia by Decreasing Receptor Phosphorylation and Enhancing Gene Regulation
- PMID: 38201570
- PMCID: PMC10778422
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16010143
PI3Kδ Inhibition Potentiates Glucocorticoids in B-lymphoblastic Leukemia by Decreasing Receptor Phosphorylation and Enhancing Gene Regulation
Abstract
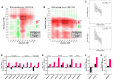
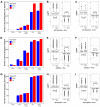
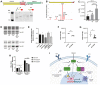
Glucocorticoids are the cornerstone of B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) therapy. Because response to glucocorticoids alone predicts overall outcomes for B-ALL, enhancing glucocorticoid potency should improve treatment. We previously showed that inhibition of the lymphoid-restricted PI3Kδ with idelalisib enhances glucocorticoid activity in B-ALL cells. Here, we show that idelalisib enhances glucocorticoid potency in 90% of primary B-ALL specimens and is most pronounced at sub-saturating doses of glucocorticoids near the EC50. Potentiation is associated with enhanced regulation of all glucocorticoid-regulated genes, including genes that drive B-ALL cell death. Idelalisib reduces phosphorylation of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) at PI3Kδ/MAPK1 (ERK2) targets S203 and S226. Ablation of these phospho-acceptor sites enhances sensitivity to glucocorticoids with ablation of S226 in particular reducing synergy. We also show that phosphorylation of S226 reduces the affinity of GR for DNA in vitro. We propose that PI3Kδ inhibition improves glucocorticoid efficacy in B-ALL in part by decreasing GR phosphorylation, increasing DNA binding affinity, and enhancing downstream gene regulation. This mechanism and the response of patient specimens suggest that idelalisib will benefit most patients with B-ALL, but particularly patients with less responsive, including high-risk, disease. This combination is also promising for the development of less toxic glucocorticoid-sparing therapies.
Keywords: chemotherapy; drug resistance; glucocorticoids; neoplasia-lymphoid leukemias; pediatric hematology/oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
J.A.O.Z. discloses spouse employment at Integrated DNA Technologies. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Update of
-
PI3Kδ inhibition potentiates glucocorticoids in B-lymphoblastic leukemia by decreasing receptor phosphorylation and enhancing gene regulation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 11:2023.02.10.527869. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.10.527869. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 27;16(1):143. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010143. PMID: 36798391 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
PI3Kδ inhibition potentiates glucocorticoids in B-lymphoblastic leukemia by decreasing receptor phosphorylation and enhancing gene regulation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 11:2023.02.10.527869. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.10.527869. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 27;16(1):143. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010143. PMID: 36798391 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Suppression of B-cell development genes is key to glucocorticoid efficacy in treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2017 Jun 1;129(22):3000-3008. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-02-766204. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28424165 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation differentially affects target gene expression.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Aug;22(8):1754-66. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0219. Epub 2008 May 15. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18483179 Free PMC article.
-
Idelalisib: A Novel PI3Kδ Inhibitor for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Ann Pharmacother. 2015 Oct;49(10):1162-70. doi: 10.1177/1060028015594813. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Ann Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26185276 Review.
-
Glucocorticoid receptors and resistance to glucocorticoids in hematologic malignancies.Leuk Lymphoma. 1994 Nov;15(5-6):363-74. doi: 10.3109/10428199409049738. Leuk Lymphoma. 1994. PMID: 7873993 Review.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Childhood Leukemia. [(accessed on 3 October 2023)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/childleuk.html.
-
- Schrappe M., Arico M., Harbott J., Biondi A., Zimmermann M., Conter V., Reiter A., Valsecchi M.G., Gadner H., Basso G., et al. Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Good initial steroid response allows early prediction of a favorable treatment outcome. Blood. 1998;92:2730–2741. - PubMed
-
- de Vries M.A.G., van Litsenburg R.R.L., Huisman J., Grootenhuis M.A., Versluys A.B., Kaspers G.J.L., Gemke R.J.B.J. Effect of dexamethasone on quality of life in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: A prospective observational study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes. 2008;6:103. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-6-103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

