OGG1 as an Epigenetic Reader Affects NFκB: What This Means for Cancer
- PMID: 38201575
- PMCID: PMC10778025
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16010148
OGG1 as an Epigenetic Reader Affects NFκB: What This Means for Cancer
Abstract
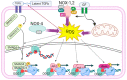
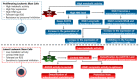
8-oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (OGG1), which was initially identified as the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the DNA base excision repair pathway, is now also recognized as a modulator of gene expression. What is important for cancer is that OGG1 acts as a modulator of NFκB-driven gene expression. Specifically, oxidant stress in the cell transiently halts enzymatic activity of substrate-bound OGG1. The stalled OGG1 facilitates DNA binding of transactivators, such as NFκB to their cognate sites, enabling the expression of cytokines and chemokines, with ensuing recruitment of inflammatory cells. Recently, we highlighted chief aspects of OGG1 involvement in regulation of gene expression, which hold significance in lung cancer development. However, OGG1 has also been implicated in the molecular underpinning of acute myeloid leukemia. This review analyzes and discusses how these cells adapt through redox-modulated intricate connections, via interaction of OGG1 with NFκB, which provides malignant cells with alternative molecular pathways to transform their microenvironment, enabling adjustment, promoting cell proliferation, metastasis, and evading killing by therapeutic agents.
Keywords: EMT; NFκB; OGG1; acute myeloid leukemia; cancer stem cells; gene regulation; innate immunity; lung cancer; microenvironment; oxidant stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vlahopoulos S.A., Cen O., Hengen N., Agan J., Moschovi M., Critselis E., Adamaki M., Bacopoulou F., Copland J.A., Boldogh I., et al. Dynamic Aberrant NF-κB Spurs Tumorigenesis: A New Model Encompassing the Microenvironment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015;26:389–403. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.06.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

