Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Copper Mesh Coated with Bamboo Cellulose Hydrogel for Efficient Oil/Water Separation
- PMID: 38201679
- PMCID: PMC10780632
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16010014
Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Copper Mesh Coated with Bamboo Cellulose Hydrogel for Efficient Oil/Water Separation
Abstract
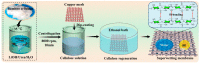
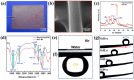
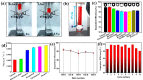
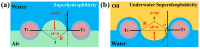
Super-wetting interface materials have shown great potential for applications in oil-water separation. Hydrogel-based materials, in particular, have been extensively studied for separating water from oily wastewater due to their unique hydrophilicity and excellent anti-oil effect. In this study, a superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic bamboo cellulose hydrogel-coated mesh was fabricated using a feasible and eco-friendly dip-coating method. The process involved dissolving bamboo cellulose in a green alkaline/urea aqueous solvent system, followed by regeneration in ethanol solvent, without the addition of surface modifiers. The resulting membrane exhibited excellent special wettability, with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity, enabling oil-water separation through a gravity-driven "water-removing" mode. The super-wetting composite membrane demonstrated a high separation efficiency of higher than 98% and a permeate flux of up to 9168 L·m-2·h-1 for numerous oil/water mixtures. It also maintained a separation efficiency of >95% even after 10 cycles of separation, indicating its long-term stability. This study presents a green, simple, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly approach for fabricating superhydrophilic surfaces to achieve oil-water separation. It also highlights the potential of bamboo-based materials in the field of oil-water separation.
Keywords: bamboo cellulose; hydrogel coating; oil/water separation; wetting.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Facile preparation of marine carrageenan hydrogel-coated steel mesh with superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic performance for highly efficient oil-water separation.Water Environ Res. 2025 Jan;97(1):e70006. doi: 10.1002/wer.70006. Water Environ Res. 2025. PMID: 39806543
-
Strong cellulose hydrogel as underwater superoleophobic coating for efficient oil/water separation.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Feb 1;229:115467. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115467. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 31826446
-
Micro/Nanoscale Structured Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Hybrid-Coated Mesh for High-Efficiency Oil/Water Separation.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jun 19;12(6):1378. doi: 10.3390/polym12061378. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575503 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose-based special wetting materials for oil/water separation: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Aug 31;185:890-906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.167. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34214576 Review.
-
Multifunctional membranes with super-wetting characteristics for oil-water separation and removal of hazardous environmental pollutants from water: A review.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020 Nov;285:102276. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102276. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020. PMID: 33039840 Review.
References
-
- Deng Y., Peng C., Dai M., Lin D., Ali I., Alhewairini S.S., Zheng X., Chen G., Li J., Naz I. Recent development of super-wettable materials and their applications in oil-water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;266:121624. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121624. - DOI
-
- Tummons E., Han Q., Tanudjaja H.J., Hejase C.A., Chew J.W., Tarabara V.V. Membrane fouling by emulsified oil: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020;248:116919. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116919. - DOI
-
- Zhang J., Liu L., Si Y., Yu J., Ding B. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes: An effective arsenal for the purification of emulsified oily wastewater. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:2002192. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002192. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

