Biomimetic Materials Based on Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate and Chlorophyll Derivatives
- PMID: 38201766
- PMCID: PMC10780539
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16010101
Biomimetic Materials Based on Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate and Chlorophyll Derivatives
Abstract
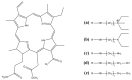
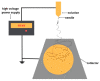
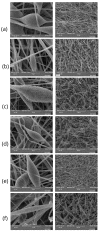
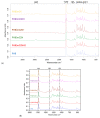
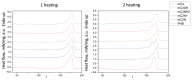
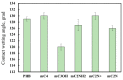
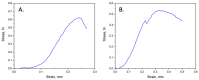
Electrospinning of biomimetic materials is of particular interest due to the possibility of producing flexible layers with highly developed surfaces from a wide range of polymers. Additionally, electrospinning is characterized by a high simplicity of implementation and the ability to modify the produced fibrous materials, which resemble structures found in living organisms. This study explores new electrospun materials based on polyhydroxyalkanoates, specifically poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, modified with chlorophyll derivatives. The research investigates the impact of chlorophyll derivatives on the morphology, supramolecular structure, and key properties of nonwoven materials. The obtained results are of interest for the development of new flexible materials with low concentrations of chlorophyll derivatives.
Keywords: antibacterial properties; chlorophyll derivatives; electrospinning; poly-3-hydroxybutyrate; supramolecular structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lukyanets E.A. The key role of peripheral substituents in the chemistry of phthalocyanines and their analogs. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines. 2010;14:40. doi: 10.1142/S1088424610001799. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

