New Physico-Chemical Analysis of Magnesium-Doped Hydroxyapatite in Dextran Matrix Nanocomposites
- PMID: 38201790
- PMCID: PMC10780894
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16010125
New Physico-Chemical Analysis of Magnesium-Doped Hydroxyapatite in Dextran Matrix Nanocomposites
Abstract
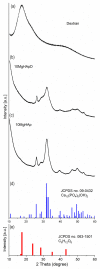
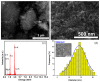
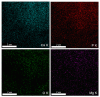
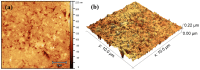
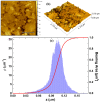
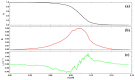
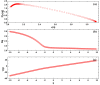
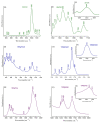
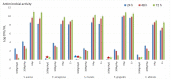
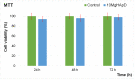
The new magnesium-doped hydroxyapatite in dextran matrix (10MgHApD) nanocomposites were synthesized using coprecipitation technique. A spherical morphology was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) characterization results show hydroxyapatite hexagonal phase formation. The element map scanning during the EDS analysis revealed homogenous distribution of constituent elements of calcium, phosphor, oxygen and magnesium. The presence of dextran in the sample was revealed by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The antimicrobial activity of the 10MgHAPD nanocomposites was assessed by in vitro assays using Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, Streptococcus mutans ATCC 25175, Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 and Candida albicans ATCC 10231 microbial strains. The results of the antimicrobial assays highlighted that the 10MgHApD nanocomposites presented excellent antimicrobial activity against all the tested microorganisms and for all the tested time intervals. Furthermore, the biocompatibility assays determined that the 10MgHApD nanocomposites did not exhibit any toxicity towards Human gingival fibroblast (HGF-1) cells.
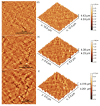
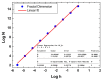
Keywords: biomedical applications; dextran; fractal features; hydroxyapatite; magnesium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest; The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of Novel Biocomposites with Antimicrobial-Activity-Based Magnesium-Doped Hydroxyapatite with Amoxicillin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;13(10):963. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100963. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452229 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Evaluation of Nanocomposite-Based Hydroxyapatite for Biomedical Applications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Nov 6;8(7):528. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8070528. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999169 Free PMC article.
-
Salvia officinalis-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposites with Antibacterial Properties.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Nov 22;15(23):4484. doi: 10.3390/polym15234484. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38231963 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the physicochemical traits, antifungal capabilities, and 3D spatial complexity of hydroxyapatite with Ag+Mg2+ substitution in the biocomposite thin films.Micron. 2024 Sep;184:103661. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2024.103661. Epub 2024 May 22. Micron. 2024. PMID: 38833994
-
New Nanobioceramics Based on Hydroxyapatite for Biomedical Applications: Stability and Properties.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;15(3):224. doi: 10.3390/nano15030224. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39940201 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Polymeric Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;16(2):249. doi: 10.3390/polym16020249. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38257048 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2019-0868, contract number 467PED⁄2020/Unitatea Executiva Pentru Finantarea Invatamantului Superior a Cercetarii Dezvoltarii si Inovarii
- Core program PC1-PN23080101/Unitatea Executiva Pentru Finantarea Invatamantului Superior a Cercetarii Dezvoltarii si Inovarii
- Contract No. T-IS 251801/04.05.2018/Independent contract
- Scientific Research Contract Nr.1/4.06.2020/Independent contract
- Código financeiro 001/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

