Molecular Pathways of Rosmarinic Acid Anticancer Activity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells: A Literature Review
- PMID: 38201832
- PMCID: PMC10780465
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16010002
Molecular Pathways of Rosmarinic Acid Anticancer Activity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells: A Literature Review
Abstract
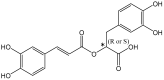
Breast cancer is the most frequent type of cancer in women. Oncogenic transcription factors promote the overproduction of cellular adhesion molecules and inflammatory cytokines during cancer development. Cancer cells exhibit significant upregulation of antiapoptotic proteins, resulting in increased cell survival, tumor growth, and metastasis. Research on the cell cycle-mediated apoptosis pathway for drug discovery and therapy has shown promising results. In fact, dietary phytoconstituents have been extensively researched for anticancer activity, providing indirect protection by activating endogenous defense systems. The role of polyphenols in key cancer signaling pathways could shed light on the underlying mechanisms of action. For instance, Rosmarinic Acid, a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, has shown potent chemoprotective properties. In this review, we present recent progress in the investigation of natural products as potent anticancer agents, with a focus on the effect of Rosmarinic Acid on triple-negative BC cell lines resistant to hormone therapy. We highlight a variety of integrated chemical biology approaches aimed at utilizing relevant mechanisms of action that could lead to significant clinical advances in BC treatment.
Keywords: antioxidants; breast cancer; natural products; polyphenols; rosmarinic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Meirelles L.E.F., Souza M.V.F., Carobeli L.R., Morelli F., Mari N.L., Damke E., Shinobu Mesquita C.S., Teixeira J.J.V., Consolaro M.E.L., Silva V. Combination of Conventional Drugs with Biocompounds Derived from Cinnamic Acid: A Promising Option for Breast Cancer Therapy. Biomedicines. 2023;11:275. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

