Exploring the Impact of Onobrychis cornuta and Veratrum lobelianum Extracts on C. elegans: Implications for MAPK Modulation, Germline Development, and Antitumor Properties
- PMID: 38201838
- PMCID: PMC10780469
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16010008
Exploring the Impact of Onobrychis cornuta and Veratrum lobelianum Extracts on C. elegans: Implications for MAPK Modulation, Germline Development, and Antitumor Properties
Abstract
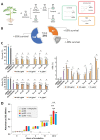
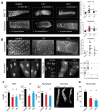
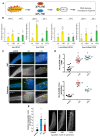
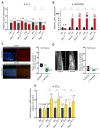
In an era of increasing interest in the potential health benefits of medicinal foods, the need to assess their safety and potential toxicity remains a critical concern. While these natural remedies have garnered substantial attention for their therapeutic potential, a comprehensive understanding of their effects on living organisms is essential. We examined 316 herbal extracts to determine their potential nematocidal attributes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Approximately 16% of these extracts exhibited the capacity to induce diminished survival rates and larval arrest, establishing a correlation between larval arrest and overall worm viability. Certain extracts led to an unexpected increase in male nematodes, accompanied by a discernible reduction in DAPI-stained bivalent structures and perturbed meiotic advancement, thereby disrupting the conventional developmental processes. Notably, Onobrychis cornuta and Veratrum lobelianum extracts activated a DNA damage checkpoint response via the ATM/ATR and CHK-1 pathways, thus hindering germline development. Our LC-MS analysis revealed jervine in V. lobelianum and nine antitumor compounds in O. cornuta. Interestingly, linoleic acid replicated phenotypes induced by O. cornuta exposure, including an increased level of pCHK-1 foci, apoptosis, and the MAPK pathway. Mutants in the MAPK pathway mitigated the decline in worm survival, underscoring its importance in promoting worm viability. This study reveals complex interactions between herbal extracts and C. elegans processes, shedding light on potential antitumor effects and mechanisms. The findings provide insights into the complex landscape of herbal medicine's impact on a model organism, offering implications for broader applications.
Keywords: DNA repair; O. cornuta; V. lobelianum; germline; linoleic acid; meiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Torenia sp. Extracts Contain Multiple Potent Antitumor Compounds with Nematocidal Activity, Triggering an Activated DNA Damage Checkpoint and Defective Meiotic Progression.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 10;17(5):611. doi: 10.3390/ph17050611. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794181 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Lappula patula Extracts on Germline Development and DNA Damage Responses in C. elegans.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;18(1):89. doi: 10.3390/ph18010089. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861152 Free PMC article.
-
Functional dissection of Caenorhabditis elegans CLK-2/TEL2 cell cycle defects during embryogenesis and germline development.PLoS Genet. 2009 Apr;5(4):e1000451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000451. Epub 2009 Apr 10. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19360121 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for studying the DNA damage response in the Caenorhabdatis elegans germ line.Methods Cell Biol. 2012;107:321-52. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394620-1.00011-4. Methods Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22226529 Review.
-
DNA repair.WormBook. 2006 Jan 13:1-12. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.54.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Extract-Induced DNA Damage, Apoptosis, and Antioxidant Effects of C. elegans: A Comparative Study of Mentha longifolia, Scrophularia orientalis, and Echium biebersteinii.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;18(7):1030. doi: 10.3390/ph18071030. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732318 Free PMC article.
-
Torenia sp. Extracts Contain Multiple Potent Antitumor Compounds with Nematocidal Activity, Triggering an Activated DNA Damage Checkpoint and Defective Meiotic Progression.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 10;17(5):611. doi: 10.3390/ph17050611. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794181 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Lappula patula Extracts on Germline Development and DNA Damage Responses in C. elegans.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;18(1):89. doi: 10.3390/ph18010089. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Report M.A. Medical Foods Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Route of Administration (Oral, Enteral), By Product (Pills, Powder, Liquid), By Application, By Sales Channel, And Segment Forecasts, 2022–2030. 2020. [(accessed on 13 December 2023)]. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/medical-foods-market.
-
- Shaul N.C., Jordan J.M., Falsztyn I.B., Baugh L.R. Insulin/IGF-dependent Wnt signaling promotes formation of germline tumors and other developmental abnormalities following early-life starvation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 2022;223:iyac173. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac173. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

