Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer's Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study
- PMID: 38201846
- PMCID: PMC10780998
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16010016
Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer's Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study
Abstract
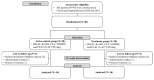
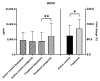
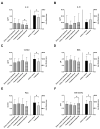
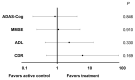
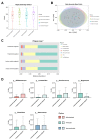
The role of neurotrophic factors, oxidative stress, and inflammation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been explored. Animal studies have reported the positive effects of probiotics on these factors. Some clinical studies also support the potential role of probiotics in improving cognitive function via the gut-brain axis in older adults. However, clinical experimental studies evaluating the efficacy of probiotics targeting the neurotrophic factors and inflammatory biomarkers, particularly among AD patients, remain very limited. In this randomized, double-blinded, active-controlled trial, we used multi-strain probiotic supplements, including Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis BLI-02, B. breve Bv-889, B. animalis subsp. lactis CP-9, B. bifidum VDD088, and Lactobacillus plantarum PL-02 as the intervention. Participants were divided into an active control group (received probiotic supplements containing 5 × 107 colony-forming units per day, CFU/day) and a treatment group (1 × 1010 CFU/day). Student's t test was applied as the main method of statistical analysis. After 12 weeks of intervention, the treatment group demonstrated a 36% increase in serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (* p = 0.005), a reduction in IL-1β (* p = 0.041), and an increase in antioxidant superoxide dismutase (SOD) (* p = 0.012). No significant change was found in the active control group. A trend toward less cognitive deterioration was observed, but not statistically significant. In conclusion, this study presents evidence supporting the benefits of multi-strain probiotics in enhancing BDNF, ameliorating inflammation and oxidative stress in AD patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; anti-inflammation; brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); clinical trial; cognitive function; oxidative stress; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The funder Glac Biotech Co., Ltd. provided financial support in the form of salaries for Y.-C.H., Y.-Y.H., S.-Y.T., Y.-W.K., J.-H.L., H.-H.H., J.-F.C. and K.-C.H., but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia 2017–2025. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Status Report on the Public Health Response to Dementia. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- Serrano-Pozo A., William C.M., Ferrer I., Uro-Coste E., Delisle M.B., Maurage C.A., Hock C., Nitsch R.M., Masliah E., Growdon J.H., et al. Beneficial effect of human anti-amyloid-beta active immunization on neurite morphology and tau pathology. Brain. 2010;133:1312–1327. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq056. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santoro A., Siviero P., Minicuci N., Bellavista E., Mishto M., Olivieri F., Marchegiani F., Chiamenti A.M., Benussi L., Ghidoni R., et al. Effects of donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine in 938 Italian patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A prospective, observational study. CNS Drugs. 2010;24:163–176. doi: 10.2165/11310960-000000000-00000. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

