Protective Effect of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (Jackfruit) Polysaccharides on Liver Injury Induced by Cyclophosphamide in Mice
- PMID: 38201995
- PMCID: PMC10780714
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16010166
Protective Effect of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (Jackfruit) Polysaccharides on Liver Injury Induced by Cyclophosphamide in Mice
Abstract
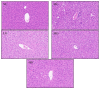
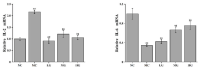
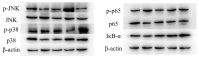
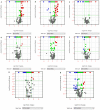
In recent years, Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (jackfruit) polysaccharides (namely JFP-Ps) have attracted much attention due to their multiple biological activities. This study aimed to explore the protective effects and the underlying mechanisms of JFP-Ps on cyclophosphamide (Cp)-induced liver damage. The protective effect of JFP-Ps was evaluated using HE staining, antioxidant testing, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), Western blot and ultra-performance liquid chromatography equipped with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) metabolomics analysis. The results showed that Cp caused pathological liver damage, activated oxidative stress and downregulated cytokine expression, while JFP-Ps treatment was found to exert antioxidant effects and play immune regulatory roles through mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor-κB (MAPK/NF-κB) related inflammation and cell apoptosis pathways to protect the Cp-induced liver injury. Metabolomic results showed that the liver-protective effects of JFP-Ps were mainly related to aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) biosynthesis, sphingolipid metabolism, purine metabolism and the citrate cycle. These results indicate that JFP-Ps have great potential application in alleviating liver injury.
Keywords: jackfruit polysaccharides; liver injury; metabolomics; protective effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Polysaccharides from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (jackfruit) pulp improves intestinal barrier functions of high fat diet-induced obese rats.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 3;9:1035619. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1035619. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36407513 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (Jackfruit) Pulp Ameliorates Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Enteritis in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 29;25(3):1661. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031661. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338941 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical properties and in vitro antioxidant activities of polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. pulp.Carbohydr Polym. 2017 Jan 2;155:354-361. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.074. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Carbohydr Polym. 2017. PMID: 27702522
-
Recent developments in Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. (jackfruit) polysaccharides: Nutritional values, structural characteristics and health benefits.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;309(Pt 2):142923. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142923. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40203947 Review.
-
Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) in health and disease: a critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(23):6344-6378. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2031094. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35144492 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional foods and bioactive compounds: a comprehensive review on their role in mitigating drug-induced liver injury.Front Nutr. 2025 May 21;11:1499697. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1499697. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40469945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

