Understanding the Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Healthy Eating among Adolescents in Chongqing, China: An Empirical Study Utilizing Structural Equation Modeling
- PMID: 38201997
- PMCID: PMC10780587
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16010167
Understanding the Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Healthy Eating among Adolescents in Chongqing, China: An Empirical Study Utilizing Structural Equation Modeling
Abstract
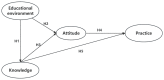
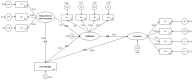
Healthy eating is crucial for optimal growth, development, and the prevention of chronic diseases in adolescents. Our study aimed to develop a comprehensive structural equation model (SEM) to analyze the relationships between knowledge, attitudes, practices (KAP), and healthy eating among adolescents in Chongqing. An online questionnaire was administered to middle school students in 39 districts and counties of Chongqing, China from 2 December to 15 December 2021 to collect sociodemographic and KAP information. SEM models were constructed to examine the relationships between educational environment and healthy eating knowledge, attitudes, and practices. The Monte Carlo test was employed to assess the significance of the mediating effect of relevant variables. The study included 139,832 adolescents aged 14.8 ± 0.7 years, with a 14% rate of overweight and obesity. Health and nutrition knowledge averaged a score of 3.60 ± 1.50 (correct rate: 60%). Participants had positive attitudes (average score: 13.61 ± 2.29) and engaged in healthy eating practices (average score: 12.06 ± 3.08). The results of the SEM revealed a significant influence of the educational environment on adolescents' knowledge (β = 0.235, p < 0.001) and attitude towards healthy eating (β = 0.143, p < 0.001). Knowledge exhibited positive effects on both attitude (β = 0.225, p < 0.001) and practice (β = 0.054, p < 0.001), while attitude exhibited positive effects on practice behavior (β = 0.565, p < 0.001). The indirect effect of knowledge on practices through attitude was more substantial than the direct effect (ratio 2.361). Our study highlights the mediating role of attitude between healthy eating knowledge and practices. A significant association exists between a favorable educational environment and improved knowledge and positive attitudes toward healthy eating among adolescents. In the future, nutrition and health education should prioritize exploring effective ways to translate knowledge into practices.
Keywords: adolescents; attitudes; healthy eating; knowledge; practices; structural equation modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Adolescent Health. [(accessed on 28 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/adolescent-health#tab=tab_1.
-
- Hollis J.L., Collins C.E., DeClerck F., Chai L.K., McColl K., Demaio A.R. Defining healthy and sustainable diets for infants, children and adolescents. Glob. Food Secur. 2020;27:100401. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100401. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

