Evaluation of a Modified Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Intervention for Adults with Cerebral Palsy and Anxiety and/or Emotion Regulation Difficulties-A Randomised Control Trial
- PMID: 38202008
- PMCID: PMC10779681
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010001
Evaluation of a Modified Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Intervention for Adults with Cerebral Palsy and Anxiety and/or Emotion Regulation Difficulties-A Randomised Control Trial
Abstract
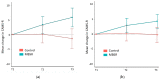
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) has not yet been evaluated for people with cerebral palsy (CP). The aims of this randomised control trial were to investigate whether a modified telehealth MBSR program could improve mindfulness and reduce depression, anxiety, and emotion regulation difficulties among adults with CP with elevated anxiety and/or emotional regulation difficulties. Participants (n = 31) with elevated anxiety and/or emotion regulation difficulties and no/mild intellectual impairment were randomised to a modified telehealth MBSR program (90 min weekly, 9 weeks) group or a wait-list group. Measurements were collected prior to (T1), after (T2), and 8 weeks post-intervention (T3). The primary outcome was the mean between-group difference in the change in Cognitive and Affective Mindfulness Scale-R (CAMS-R) scores in T1-T2. The secondary outcomes included mean within-group differences over time for the CAMS-R total scores, Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale-21 subscales, and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS) total t-score. We found no statistically significant between-group difference in mean change in mindfulness scores for T1-T2 (primary outcome). Secondary outcomes: The MBSR intervention group had improved CAMS-R scores with respect to T1-T2 and T1-T3; improved mean scores for Depression and Stress subscales for T1-T2; and improved DERS t-scores for T1-T2 and T1-T3. In conclusion, this study found no significant between-group difference for the primary outcome of mindfulness. The MBSR program was successfully modified for adults with CP and was effective in improving depression, stress, and emotion regulation. ACTRN12621000960853.
Keywords: anxiety; cerebral palsy; emotion regulation; mindfulness; mindfulness-based stress reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A randomized, controlled trial of mindfulness-based stress reduction in HIV infection.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Oct;73:331-339. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 May 26. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 29842903 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Emotion Regulation Is Associated with Anxiety, Depression and Stress in Adults with Cerebral Palsy.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 28;12(7):2527. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072527. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048620 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Training in Surgery: Additional Analysis of the Mindful Surgeon Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 May 3;2(5):e194108. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4108. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31125095 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) program on depression, emotion regulation, and sleep problems: A randomized controlled trial study on depressed elderly.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 23;24(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17759-9. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38263131 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on depression, anxiety, and stress in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2019 Jun;28(3):635-656. doi: 10.1111/inm.12568. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30656813
Cited by
-
Activity-based mindfulness: large-scale assessment of an online program on perceived stress and mindfulness.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1469316. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1469316. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39474093 Free PMC article.
-
Gender Differences in Coping Strategies and Life Satisfaction Following Cognitive-Behavioral and Mindfulness-Based Intervention for Crohn's Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 26;14(5):1569. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051569. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenbaum P., Paneth N., Leviton A., Goldstein M., Bax M., Damiano D., Dan B., Jacobsson B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007;109:8–14. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

