A Scoping Review of Measurement Tools Evaluating Awareness and Disease-Related Knowledge in Peripheral Arterial Disease Patients
- PMID: 38202114
- PMCID: PMC10780123
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010107
A Scoping Review of Measurement Tools Evaluating Awareness and Disease-Related Knowledge in Peripheral Arterial Disease Patients
Abstract
Background: Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is the third leading cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular morbidity worldwide, with high prevalence and associated complications, and is often overlooked and undertreated. Research has shown that there is a profound lack of PAD-related knowledge and awareness; additionally, information sources are not often reliable and accessible. The objective of this scoping review was: (1) to identify and critically appraise instruments that measure patients' disease-related knowledge/awareness about PAD, and (2) to characterize the current state of knowledge/awareness levels among these patients.
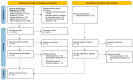
Methods: This systematic review was conducted and reported in accordance with the PRISMA statement. Six databases (APA PsycInfo, CINAHL Ultimate, Embase, Emcare Nursing, Medline ALL and Web of Science Core Collection) were searched, and search strategies were developed utilizing the PICO framework. Potential studies of any methodological design were considered for inclusion through a snowball hand search. Data from the included articles were extracted by a reviewer, and the extraction accuracy was independently cross-checked by another author.
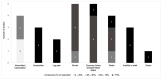
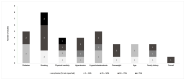
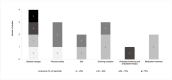
Results: The initial database search yielded 9832 records, of which sixteen studies (thirteen quantitative and three qualitative) were included. Only three questionnaires had their psychometric properties assessed. Questionnaire items focused on the following topics: definition/characteristics, risk factors/causes, treatment, complications, and personal issues regarding the perception/management of the disease. Overall, knowledge/awareness about PAD was low among patients.
Conclusions: This study identified major gaps in PAD education, including the lack of availability of a validated measurement tool addressing all educational topics relevant to care and low knowledge/awareness of patients about their condition.
Keywords: awareness; knowledge; patient education as topic; peripheral artery disease; surveys and questionnaires.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Health Literacy and Disease Knowledge of Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease or Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Scoping Review.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2024 Jun;67(6):935-947. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2024.03.040. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 38552837
-
Inpatient vs. Outpatient: A Systematic Review of Information Needs throughout the Heart Failure Patient Journey.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 14;13(4):1085. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041085. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38398398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
-
Stenting for peripheral artery disease of the lower extremities: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(18):1-88. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fowkes F.G.R., Rudan D., Rudan I., Aboyans V., Denenberg J.O., McDermott M.M., Norman P.E., Sampson U.K.A., Williams L.J., Mensah G.A., et al. Comparison of Global Estimates of Prevalence and Risk Factors for Peripheral Artery Disease in 2000 and 2010: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Lancet. 2013;382:1329–1340. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61249-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Clinical Guideline Centre . Lower Limb Peripheral Arterial Disease: Diagnosis and Management. National Clinical Guideline Centre; London, UK: 2012. NICE Clinical Guidelines.
-
- Gerhard-Herman M.D., Gornik H.L., Barrett C., Barshes N.R., Corriere M.A., Drachman D.E., Fleisher L.A., Fowkes F.G.R., Hamburg N.M., Kinlay S., et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients with Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: Executive Summary. Vasc. Med. 2017;22:NP1–NP43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hirsch A.T., Murphy T.P., Lovell M.B., Twillman G., Treat-Jacobson D., Harwood E.M., Mohler E.R., Creager M.A., Hobson R.W., Robertson R.M., et al. Gaps in Public Knowledge of Peripheral Arterial Disease: The First National PAD Public Awareness Survey. Circulation. 2007;116:2086–2094. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.725101. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

