Anti-Inflammatory and Cortical Responses after Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Disorders of Consciousness: An Exploratory Study
- PMID: 38202115
- PMCID: PMC10779892
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010108
Anti-Inflammatory and Cortical Responses after Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Disorders of Consciousness: An Exploratory Study
Abstract
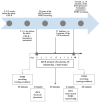
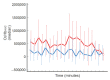
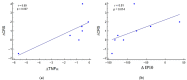
Disorders of consciousness (DoC) due to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) are associated with severe disability and an alteration of cortical activation, angiogenesis, and inflammation, which are crucial elements for behavioural recovery. This exploratory study aimed to evaluate anti-inflammatory and cortical responses after transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in traumatic prolonged disorders of consciousness. Ten minimally conscious state (MCS) patients underwent ten sessions of anodal tDCS (five sessions/week, two weeks, 40 min/session) on the primary motor cortex bilaterally. Clinical evaluations were performed using the Coma Recovery Scale-Revised (CRS-R) pre- and post-treatment. In contrast, after single and multiple tDCS sessions, the haemodynamic cortical response was obtained with functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). Moreover, angiogenesis (angiopoietin-2, BMP9, endoglin, HbEFG, HGF, IL8, Leptin, PLGF, VEGF-A, and VEGF-C) and inflammation (GM-CSF, IFNg, IP10, MCP1, and TNFα) circulating biomarkers were collected. A significant haemodynamic response was observed after a single tDCS session, with an increased activation from 4.4 (3.1-6.1) to 7.6 (2.9-15.7) a.u. (p = 0.035). After ten tDCS sessions, a significant reduction of angiopoietin-2, VEGF-C, and IP-10 was detected. Moreover, a correlation between behavioural (CRS-R), TNFα (r = 0.89; p = 0.007), and IP10 (r = 0.81; p = 0.014) variation was found. In conclusion, a single tDCS session can increase the cortical activation in MCS patients. Moreover, multiple tDCS sessions showed an anti-inflammatory effect related to behavioural improvement.
Keywords: biomarkers; disorders of consciousness; fNIRS; inflammation; tDCS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study’s design, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Laureys S., Celesia G.G., Cohadon F., Lavrijsen J., León-Carrión J., Sannita W.G., Sazbon L., Schmutzhard E., von Wild K.R., Zeman A., et al. Unresponsive Wakefulness Syndrome: A New Name for the Vegetative State or Apallic Syndrome. BMC Med. 2010;8:68. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-68. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

