Intrathecal Morphine and Post-Operative Pain Relief in Robotic Surgeries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38202144
- PMCID: PMC10779813
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010137
Intrathecal Morphine and Post-Operative Pain Relief in Robotic Surgeries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Despite the potential benefits of intrathecal morphine (ITM), the precise role and dosing of ITM in robotic assisted surgery (RAS) remains unclear. This systematic review explores real-world evidence to evaluate the efficacy and outcomes of ITM in patients undergoing RAS. In accordance with PRISMA guidelines, a comprehensive search was conducted on four databases: MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Library and APA PsycInfo. Primary outcomes included pain scores at rest and on exertion at 24- and 48-h time intervals, and secondary outcomes aimed to explore the side effects of ITM. A meta-analysis was conducted to determine mean differences. A risk of bias assessment was conducted via the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool. A total of 9 RCTs involving 619 patients were included in this review, of which 298 patients were administered ITM. Significant pain score reductions were observed both at rest (MD = -27.15; 95% CI [-43.97, -10.33]; I2 = 95%; p = 0.002) and on exertion (MD = -25.88; 95% CI [-37.03, -14.72]; I2 = 79%; p = 0.0003) 24 h postoperatively in the ITM groups, accompanied by a notable decrease in postoperative IV morphine equivalent consumption at 24 h (MD = -20.13; 95% CI [-30.74, -9.52]; I2 = 77%; p = 0.0002). ITM improved pain scores both at rest and on exertion at 24 and 48 h intervals, concurrently reducing the need for postoperative opioid consumption, but at the cost of an increased incidence of adverse events.
Keywords: intrathecal morphine; post-operative outcomes; robotic surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
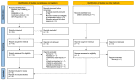


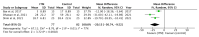

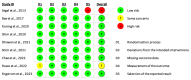
References
-
- Santonocito C., Bartolotta N., Lanzafame B., Morgana A., Continella C., Cirica G., Astuto M., Sanfilippo F. α-2 agonists vs. fentanyl as adjuvants for spinal anesthesia in elective cesarean section: A meta-analysis. Minerva Anestesiol. 2023;89:445–454. - PubMed
-
- Cummings A., Orgill B.D., Fitzgerald B.M. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. [(accessed on 20 July 2023)]. Intrathecal Morphine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499880/ - PubMed
-
- Olawin A.M., Das J.M. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. [(accessed on 20 July 2023)]. Spinal Anesthesia. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537299/ - PubMed
-
- Cosgrave D., Shanahan E., Conlon N., Joshi M. Intrathecal Opioids: Pain Tutorial 347. [(accessed on 20 July 2023)]. Available online: https://resources.wfsahq.org/atotw/intrathecal-opioids/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

