Myocarditis and Chronic Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy, from Acute Inflammation to Chronic Inflammatory Damage: An Update on Pathophysiology and Diagnosis
- PMID: 38202158
- PMCID: PMC10780032
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010150
Myocarditis and Chronic Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy, from Acute Inflammation to Chronic Inflammatory Damage: An Update on Pathophysiology and Diagnosis
Abstract
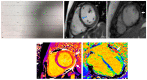
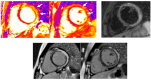
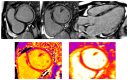
Acute myocarditis covers a wide spectrum of clinical presentations, from uncomplicated myocarditis to severe forms complicated by hemodynamic instability and ventricular arrhythmias; however, all these forms are characterized by acute myocardial inflammation. The term "chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy" describes a persistent/chronic inflammatory condition with a clinical phenotype of dilated and/or hypokinetic cardiomyopathy associated with symptoms of heart failure and increased risk for arrhythmias. A continuum can be identified between these two conditions. The importance of early diagnosis has grown markedly in the contemporary era with various diagnostic tools available. While cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) is valid for diagnosis and follow-up, endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) should be considered as a first-line diagnostic modality in all unexplained acute cardiomyopathies complicated by hemodynamic instability and ventricular arrhythmias, considering the local expertise. Genetic counseling should be recommended in those cases where a genotype-phenotype association is suspected, as this has significant implications for patients' and their family members' prognoses. Recognition of the pathophysiological pathway and clinical "red flags" and an early diagnosis may help us understand mechanisms of progression, tailor long-term preventive and therapeutic strategies for this complex disease, and ultimately improve clinical outcomes.
Keywords: endomyocardial biopsy; eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; inflammatory cardiomyopathy; myocarditis; sarcoidosis; systemic lupus erythematosus; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tschöpe C., Ammirati E., Bozkurt B., Caforio A.L.P., Cooper L.T., Felix S.B., Hare J.M., Heidecker B., Heymans S., Hübner N., et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: Current evidence and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021;18:169–193. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00435-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ammirati E., Frigerio M., Adler E.D., Basso C., Birnie D.H., Brambatti M., Friedrich M.G., Klingel K., Lehtonen J., Moslehi J.J., et al. Management of Acute Myocarditis and Chronic Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy: An Expert Consensus Document. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020;13:e007405. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.007405. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedrich M.G., Sechtem U., Schulz-Menger J., Holmvang G., Alakija P., Cooper L.T., White J.A., Abdel-Aty H., Gutberlet M., Prasad S., et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in myocarditis: A JACC White Paper. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009;53:1475–1487. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

