Management and Treatment for Dysphagia in Neurodegenerative Disorders
- PMID: 38202163
- PMCID: PMC10779554
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010156
Management and Treatment for Dysphagia in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
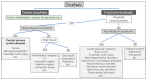
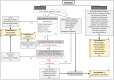
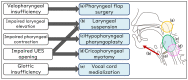
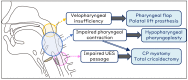
Patients with neurodegenerative disorders (NDDs) often experience functional dysphagia, which may involve dysfunction in a specific phase of swallowing or in the entire process. This review outlines the approach to dysphagia in the setting of NDDs. Distinguishing the etiology of dysphagia can be difficult, and it is important to always look out for signs pointing to NDD as the cause. Thorough diagnostic work-up is essential, and it includes a comprehensive history and physical examination, alongside swallowing function tests, such as fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing, videofluoroscopic swallowing study, and high-resolution manometry. Management requires a multidisciplinary approach with a treatment plan tailored to each patient. This involves dietary guidance, swallowing rehabilitation, and surgery in cases in which improvement with rehabilitation is inadequate. Surgery may involve altering certain pharyngolaryngeal structures to facilitate swallowing and reduce the risk of aspiration (swallowing improvement surgery) or separating the airway and digestive tract while sacrificing laryngeal function, with the main goal of preventing aspiration (aspiration prevention surgery). Proper management stems from recognizing the impact of these disorders on swallowing and consistently finding ways to improve the quality of life of patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; dysphagia; multiple system atrophy; neurodegenerative disorders; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Causes, diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic dysphagia as an interdisciplinary clinical problem].Otolaryngol Pol. 2006;60(4):491-500. Otolaryngol Pol. 2006. PMID: 17152798 Review. Polish.
-
[Evaluation and treatment of dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson's disease].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2011 Nov;51(11):1072-4. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.51.1072. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2011. PMID: 22277481 Japanese.
-
Dysphagia in Parkinson's Disease.Dysphagia. 2016 Feb;31(1):24-32. doi: 10.1007/s00455-015-9671-9. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Dysphagia. 2016. PMID: 26590572 Review.
-
Impact of Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing Outcomes and Dysphagia Management in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Laryngoscope. 2021 Apr;131(4):726-730. doi: 10.1002/lary.28791. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Laryngoscope. 2021. PMID: 32542698
-
Choice of Aspiration Prevention Surgery for Patients With Neuromuscular Disorders: Report of Three Cases.Front Surg. 2019 Nov 21;6:66. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2019.00066. eCollection 2019. Front Surg. 2019. PMID: 31824959 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Improved Pharyngeal Contraction and Oral Intake Status After Modified Central-Part Laryngectomy for Late-Stage ALS.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Jul;173(1):154-161. doi: 10.1002/ohn.1229. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40105438 Free PMC article.
-
Cause of death for patients who present with primary progressive apraxia of speech.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2025 Jul 21;138:107968. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2025.107968. Online ahead of print. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2025. PMID: 40706471
-
Vocal Fold Motion Impairment in Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 24;13(9):2507. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092507. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory Afferent Neural Circuits Mediate Electroacupuncture to Improve Swallowing Function in a Post-Stroke Dysphagia Mouse Model.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70514. doi: 10.1111/cns.70514. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40708119 Free PMC article.
-
A Challenging Case of Severe Dysphagia in Multiple System Atrophy.Dysphagia. 2025 Aug 15. doi: 10.1007/s00455-025-10871-x. Online ahead of print. Dysphagia. 2025. PMID: 40815490 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dziewas R., Allescher H.D., Aroyo I., Bartolome G., Beilenhoff U., Bohlender J., Breitbach-Snowdon H., Fheodoroff K., Glahn J., Heppner H.J., et al. Diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic dysphagia—S1 guideline of the German Society of Neurology. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021;3:23. doi: 10.1186/s42466-021-00122-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

