Short-Term Outcomes of XEN45 Standalone versus Combined with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38202164
- PMCID: PMC10780016
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010157
Short-Term Outcomes of XEN45 Standalone versus Combined with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
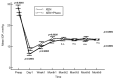
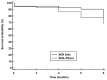
The XEN45 is a minimally invasive glaucoma surgery device commonly used in clinical practice. This retrospective study included consecutive patients with open-angle glaucoma who underwent a XEN45 implant with mitomycin C, either alone or in combination with phacoemulsification, between June 2015 and March 2021. The primary end point was the mean change in intraocular pressure (IOP) from the baseline to month 6. A total of 677 eyes, 395 (58.3%) in the XEN alone group and 282 (41.7%) in the XEN+Phaco group, were included in this study. The preoperative IOP was significantly lowered from 28.7 ± 8.6 mmHg and 25.4 ± 6.9 mmHg to 13.5 ± 5.0 mmHg and 13.5 ± 4.1 mmHg at month 6 in the XEN solo and XEN+Phaco groups, respectively, with p < 0.0001 each. The mean (95% confidence interval) number of ocular hypotensive medications was significantly reduced from 3.3 (3.2-3.4) to 0.2 (0.1-0.2) and from 3.1 (2.9-3.2) to 0.2 (0.1-0.2) in the XEN solo and XEN+Phaco groups, respectively, with p < 0.0001 each. Needling was performed in 228 (33.7%) eyes. Conclusions: the XEN implant significantly reduces both IOP and the number of ocular hypotensive medications. IOP lowering was higher in the XEN solo group than in the XEN+Phaco one, although such a difference was only evident during the first month after surgery.
Keywords: MIGS; XEN implant; intraocular pressure; needling; open-angle glaucoma; success.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-Term Effectiveness of XEN 45 Gel-Stent in Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients.Clin Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr 26;17:1223-1232. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S405821. eCollection 2023. Clin Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37131537 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effectiveness and safety of XEN45 in open-angle glaucoma patients.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 4;44(1):310. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03234-2. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38960998
-
Multicenter case series of standalone XEN implant vs. combination with phacoemulsification in Turkish patients.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Oct;41(10):3371-3379. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01899-7. Epub 2021 May 28. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34050406
-
[XEN® Gel Stent for management of chronic open angle glaucoma: A review of the literature (French translation of the article)].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019 Apr;42(4):391-403. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2018.10.005. Epub 2019 Mar 14. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019. PMID: 30879831 Review. French.
-
Ab interno trabecular bypass surgery with Trabectome for open-angle glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 4;2(2):CD011693. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011693.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33580495 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
No Changes in Keratometry Readings and Anterior Chamber Depth after XEN Gel Implantation in Patients with Glaucoma.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 26;13(9):2537. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092537. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laborda-Guirao T., Cubero-Parra J.M., Hidalgo-Torres A. Efficacy and safety of XEN 45 gel stent alone or in combination with phacoemulsification in advanced open angle glaucoma patients: 1-year retrospective study. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2020;13:1250–1256. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.08.11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

