Targeting Interleukin-17 as a Novel Treatment Option for Fibrotic Diseases
- PMID: 38202170
- PMCID: PMC10780256
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010164
Targeting Interleukin-17 as a Novel Treatment Option for Fibrotic Diseases
Abstract
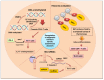
Fibrosis is the end result of persistent inflammatory responses induced by a variety of stimuli, including chronic infections, autoimmune reactions, and tissue injury. Fibrotic diseases affect all vital organs and are characterized by a high rate of morbidity and mortality in the developed world. Until recently, there were no approved antifibrotic therapies. In recent years, high levels of interleukin-17 (IL-17) have been associated with chronic inflammatory diseases with fibrotic complications that culminate in organ failure. In this review, we provide an update on the role of IL-17 in fibrotic diseases, with particular attention to the most recent lines of research in the therapeutic field represented by the epigenetic mechanisms that control IL-17 levels in fibrosis. A better knowledge of the IL-17 signaling pathway implications in fibrosis could design new strategies for therapeutic benefits.
Keywords: IL-17; autoimmune; biological drugs; epigenetics; fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

