Health and Environmental Hazards of the Toxic Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn (Bracken Fern)
- PMID: 38202326
- PMCID: PMC10780724
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13010018
Health and Environmental Hazards of the Toxic Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn (Bracken Fern)
Abstract
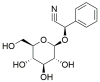
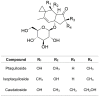
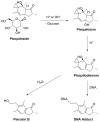
Bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn) is ubiquitous and acts as a cosmopolitan weed in pastures and similar environments. Despite its historical uses, it presents risks due to toxicity. This study, conducted in the second half of 2023, aimed to assess the environmental and health hazards of P. aquilinum, primarily focusing on its carcinogenic compound, ptaquiloside. The literature was comprehensively reviewed using diverse databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Information was synthesized from original research articles, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and relevant animal studies. Animals grazing on bracken fern face annual production losses due to toxin exposure. The substantial impact on biodiversity, animal health, and human well-being arises from the presence of ptaquiloside and related compounds in milk, meat, and water, along with the increasing global prevalence of P. aquilinum and its swift colonization in acidic soil and fire-damaged areas. The objectives were to identify major bioactive compounds and explore their effects at molecular, cellular, pathological, and population levels. Various cooking techniques were considered to mitigate toxin exposure, although complete elimination remains unattainable. Therefore, the findings emphasize the need for cautious consumption. In conclusion, continued research is necessary to better understand and manage its environmental and health implications.
Keywords: Pteridium aquilinum; bioactive compounds; bracken fern; fiddleheads; health; ptaquiloside; thiaminase; weed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A biological hazard of our age: bracken fern [Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn]--a review.Acta Vet Hung. 2009 Mar;57(1):183-96. doi: 10.1556/AVet.57.2009.1.18. Acta Vet Hung. 2009. PMID: 19457786 Review.
-
Ptaquiloside, the major carcinogen of bracken fern, in the pooled raw milk of healthy sheep and goats: an underestimated, global concern of food safety.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 May 20;63(19):4886-92. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01937. Epub 2015 May 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25932502
-
Bracken-associated human and animal health hazards: chemical, biological and pathological evidence.J Hazard Mater. 2012 Feb 15;203-204:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.046. Epub 2011 Dec 24. J Hazard Mater. 2012. PMID: 22226718 Review.
-
Pteridium aquilinum and its ptaquiloside toxin induce DNA damage response in gastric epithelial cells, a link with gastric carcinogenesis.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Mar;126(1):60-71. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr329. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22143989
-
Modeling the environmental fate of bracken toxin ptaquiloside: Production, release and transport in the rhizosphere.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Apr 15;921:170658. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170658. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38340825
Cited by
-
Toxic Threats from the Fern Pteridium aquilinum: A Multidisciplinary Case Study in Northern Spain.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7157. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157157. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806289 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacognostic evaluation and antimicrobial activity of Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn leaves (Onocleaceae) via in vitro and in silico perspectives.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 9;20(4):e0318943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318943. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40203065 Free PMC article.
-
Bracken Fern Carcinogen, Ptaquiloside, Forms a Guanine O6-Adduct in DNA.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Jan 15;73(2):1053-1061. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c07187. Epub 2025 Jan 7. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39772526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caloni F., Berny P., Croubels S., Sachana M., Guitart R. Chapter 3-Epidemiology of Animal Poisonings in Europe. In: Gupta R.C., editor. Veterinary Toxicology. 3rd ed. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2018. pp. 45–56.
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer Bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum) and some of its constituents. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risk Chem. Hum. 1986;40:47–65. - PubMed
-
- Tryon R.M. Contributions from the Gray Herbarium of Harvard University. Harvard University Herbaria; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1941. A revision of the genus Pteridium; pp. 1–67.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources