Ameliorating Effects of Graphene Oxide on Cadmium Accumulation and Eco-Physiological Characteristics in a Greening Hyperaccumulator (Lonicera japonica Thunb.)
- PMID: 38202327
- PMCID: PMC10780341
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13010019
Ameliorating Effects of Graphene Oxide on Cadmium Accumulation and Eco-Physiological Characteristics in a Greening Hyperaccumulator (Lonicera japonica Thunb.)
Abstract
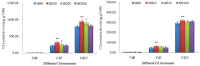
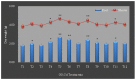
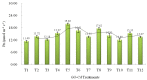
Graphene oxide (GO), as a novel carbon-based nanomaterial (CBN), has been widely applied to every respect of social life due to its unique composite properties. The widespread use of GO inevitably promotes its interaction with heavy metal cadmium (Cd), and influences its functional behavior. However, little information is available on the effects of GO on greening hyperaccumulators under co-occurring Cd. In this study, we chose a typical greening hyperaccumulator (Lonicera japonica Thunb.) to show the effect of GO on Cd accumulation, growth, net photosynthesis rate (Pn), carbon sequestration and oxygen release functions of the plant under Cd stress. The different GO-Cd treatments were set up by (0, 10, 50 and 100 mg L-1) GO and (0, 5 and 25 mg L-1) Cd in solution culture. The maximum rate of Cd accumulation in the roots and shoots of the plant were increased by 10 mg L-1 GO (exposed to 5 mg L-1 Cd), indicating that low-concentration GO (10 mg L-1) combined with low-concentration Cd (5 mg L-1) might stimulate the absorption of Cd by L. japonica. Under GO treatments without Cd, the dry weight of root and shoot biomass, Pn value, carbon sequestration per unit leaf area and oxygen release per unit leaf area all increased in various degrees, especially under 10 mg L-1 GO, were 20.67%, 12.04%, 35% and 28.73% higher than the control. Under GO-Cd treatments, it is observed that the cooperation of low-concentration GO (10 mg L-1) and low-concentration Cd (5 mg L-1) could significantly stimulate Cd accumulation, growth, photosynthesis, carbon sequestration and oxygen release functions of the plant. These results indicated that suitable concentrations of GO could significantly alleviate the effects of Cd on L. japonica, which is helpful for expanding the phytoremediation application of greening hyperaccumulators faced with coexistence with environment of nanomaterials and heavy metals.
Keywords: cadmium; graphene oxide; greening plants; hyperaccumulator; response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Cadmium Stress on Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release Characteristics in A Landscaping Hyperaccumulator-Lonicera japonica Thunb.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;12(14):2689. doi: 10.3390/plants12142689. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514303 Free PMC article.
-
Electric Field-Enhanced Cadmium Accumulation and Photosynthesis in a Woody Ornamental Hyperaccumulator-Lonicera japonica Thunb.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 11;11(8):1040. doi: 10.3390/plants11081040. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448768 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a potential hyperaccumulator--Lonicera japonica Thunb.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Sep 30;169(1-3):170-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.03.090. Epub 2009 Mar 27. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 19380199
-
Hormesis Responses of Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics in Lonicera japonica Thunb. to Cadmium Stress: Whether Electric Field Can Improve or Not?Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 18;12(4):933. doi: 10.3390/plants12040933. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840281 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cadmium hyperaccumulation on the concentrations of four trace elements in Lonicera japonica Thunb.Ecotoxicology. 2011 Jun;20(4):698-705. doi: 10.1007/s10646-011-0609-1. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Ecotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21318389
Cited by
-
Effects of cadmium (Cd) on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in the ornamental Plant Salvia splendens Ker-Gawl.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025 Mar;31(3):507-519. doi: 10.1007/s12298-025-01584-4. Epub 2025 Apr 6. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025. PMID: 40256272
-
Identification of the ZmATG18 subfamily genes in maize and the role of ZmATG18a in drought stress.BMC Genomics. 2025 Aug 26;26(1):777. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11910-5. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40859143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tripathi A., Bonilla-Cruz J. Review on healthcare biosensing nanomaterials. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023;6:5042–5074. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c00941. - DOI
-
- Wan S., Bi H.C., Sun L.T. Graphene and carbon-based nanomaterials as highly efficient adsorbents for oils and organic solvents. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016;5:3–22. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2015-0062. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

