Ion Changes and Signaling under Salt Stress in Wheat and Other Important Crops
- PMID: 38202354
- PMCID: PMC10780558
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13010046
Ion Changes and Signaling under Salt Stress in Wheat and Other Important Crops
Abstract
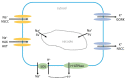
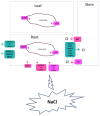
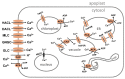
High concentrations of sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl-), calcium (Ca2+), and sulphate (SO42-) are frequently found in saline soils. Crop plants cannot successfully develop and produce because salt stress impairs the uptake of Ca2+, potassium (K+), and water into plant cells. Different intracellular and extracellular ionic concentrations change with salinity, including those of Ca2+, K+, and protons. These cations serve as stress signaling molecules in addition to being essential for ionic homeostasis and nutrition. Maintaining an appropriate K+:Na+ ratio is one crucial plant mechanism for salt tolerance, which is a complicated trait. Another important mechanism is the ability for fast extrusion of Na+ from the cytosol. Ca2+ is established as a ubiquitous secondary messenger, which transmits various stress signals into metabolic alterations that cause adaptive responses. When plants are under stress, the cytosolic-free Ca2+ concentration can rise to 10 times or more from its resting level of 50-100 nanomolar. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are linked to the Ca2+ alterations and are produced by stress. Depending on the type, frequency, and intensity of the stress, the cytosolic Ca2+ signals oscillate, are transient, or persist for a longer period and exhibit specific "signatures". Both the influx and efflux of Ca2+ affect the length and amplitude of the signal. According to several reports, under stress Ca2+ alterations can occur not only in the cytoplasm of the cell but also in the cell walls, nucleus, and other cell organelles and the Ca2+ waves propagate through the whole plant. Here, we will focus on how wheat and other important crops absorb Na+, K+, and Cl- when plants are under salt stress, as well as how Ca2+, K+, and pH cause intracellular signaling and homeostasis. Similar mechanisms in the model plant Arabidopsis will also be considered. Knowledge of these processes is important for understanding how plants react to salinity stress and for the development of tolerant crops.
Keywords: cereals; chloride; cytosolic Ca2+, K+, Na+, pH; salt stress; signaling; wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytosolic calcium and pH signaling in plants under salinity stress.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Mar;5(3):233-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.3.10740. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20037468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerium oxide nanoparticles improve cotton salt tolerance by enabling better ability to maintain cytosolic K+/Na+ ratio.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 May 25;19(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00892-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34034767 Free PMC article.
-
PDH45 transgenic rice maintain cell viability through lower accumulation of Na(+), ROS and calcium homeostasis in roots under salinity stress.J Plant Physiol. 2016 Feb 1;191:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Nov 27. J Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26687010
-
Potassium: A track to develop salinity tolerant plants.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Oct;167:1011-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.09.031. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34598021 Review.
-
Potassium-induced decrease in cytosolic Na+ alleviates deleterious effects of salt stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2019 Sep;21(5):825-831. doi: 10.1111/plb.12999. Epub 2019 May 23. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2019. PMID: 31034750
Cited by
-
Enhancing Soybean Salt Tolerance with GSNO and Silicon: A Comprehensive Physiological, Biochemical, and Genetic Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 13;26(2):609. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020609. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859323 Free PMC article.
-
Growth and physiological characteristics of forage bermudagrass in response to salt stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 1;25(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06281-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40021956 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan pre- and post-treatment modulates molecular and physiological responses to salinity in Brassica Napus L.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 2;15(1):28219. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13996-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40753266 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Defense and Ionic Homeostasis Govern Stage-Specific Response of Salinity Stress in Contrasting Rice Varieties.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 9;13(6):778. doi: 10.3390/plants13060778. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38592827 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Single Nucleotide Polymorphic Loci and Candidate Genes for Seed Germination Percentage in Okra under Salt and No-Salt Stresses by Genome-Wide Association Study.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;13(5):588. doi: 10.3390/plants13050588. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475435 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

