Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Trehalose-6-phosphate Synthase and Trehalose-6-phosphate Phosphatase Gene Families in Rose (Rosa hybrida cv 'Carola') under Different Light Conditions
- PMID: 38202423
- PMCID: PMC10780518
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13010114
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Trehalose-6-phosphate Synthase and Trehalose-6-phosphate Phosphatase Gene Families in Rose (Rosa hybrida cv 'Carola') under Different Light Conditions
Abstract
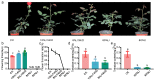
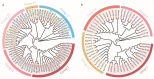
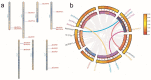
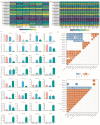
Trehalose, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS),and trehalose-6-phosphatase (TPP) have been reported to play important roles in plant abiotic stress and growth development. However, their functions in the flowering process of Rosa hybrida have not been characterized. In this study we found that, under a short photoperiod or weak light intensity, the content of trehalose in the shoot apical meristem of Rosa hybrida cv 'Carola' significantly decreased, leading to delayed flowering time. A total of nine RhTPSs and seven RhTPPs genes were identified in the genome. Cis-element analysis suggested that RhTPS and RhTPP genes were involved in plant hormones and environmental stress responses. Transcriptome data analysis reveals significant differences in the expression levels of RhTPSs and RhTPPs family genes in different tissues and indicates that RhTPPF and RhTPPJ are potential key genes involved in rose flower bud development under different light environments. The results of quantitative real-time reverse transcription (qRT-PCR) further indicate that under short photoperiod and weak light intensity all RhTPP members were significantly down-regulated. Additionally, RhTPS1a, RhTPS10, and RhTPS11 were up-regulated under a short photoperiod and showed a negative correlation with flowering time and trehalose content decrease. Under weak light intensity, RhTPS11 was up-regulated and negatively regulated flowering, while RhTPS5, RhTPS6, RhTPS7b, RhTPS9, and RhTPS10 were down-regulated and positively regulated flowering. This work lays the foundation for revealing the functions of RhTPS and RhTPP gene families in the regulation of rose trehalose.
Keywords: Rosa hybrida; flowering; photoperiod and light intensity responses; trehalose; trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene; trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RhLHY-RhTPPF-Tre6P Inhibits Flowering in Rosa hybrida Under Insufficient Light by Regulating Sugar Distribution.Plant Cell Environ. 2025 Jan;48(1):489-510. doi: 10.1111/pce.15157. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Plant Cell Environ. 2025. PMID: 39282808
-
Genome-wide identification of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) and expression analysis in response to phytohormones and abiotic stresses.PeerJ. 2022 Sep 9;10:e13934. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13934. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36105645 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and expression pattern of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene families in Populus.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Sep 30;187:9-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.096. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34298047
-
Metabolic analysis of the regulatory mechanism of sugars on secondary flowering in Magnolia.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Dec 14;23(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12860-022-00458-x. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36517772 Free PMC article.
-
Invertebrate Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene: Genetic Architecture, Biochemistry, Physiological Function, and Potential Applications.Front Physiol. 2018 Jan 31;9:30. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00030. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29445344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paeonia genus: a systematic review of active ingredients, pharmacological effects and mechanisms, and clinical applications for the treatment of cancer.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Sep;47(8-9):677-695. doi: 10.1007/s12272-024-01512-2. Epub 2024 Sep 22. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 39306813
-
Harnessing de novo transcriptome sequencing to identify and characterize genes regulating carbohydrate biosynthesis pathways in Salvia guaranitica L.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Sep 26;15:1467432. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1467432. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39391775 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the WOX gene family and function exploration of RhWOX331 in rose (R. 'The Fairy').Front Plant Sci. 2024 Sep 3;15:1461322. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1461322. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39290741 Free PMC article.
-
MYC2 influences rubber and sesquiterpene lactones synthesis in Taraxacum species.Planta. 2025 May 24;262(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04719-9. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40413374 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of three novel stem rot pathogens and their antagonistic endophytic bacteria associated with Cistanche deserticola.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Apr 8;206(5):208. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03946-0. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38587620
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

