The Antifungal Activities of Silver Nano-Aggregates Biosynthesized from the Aqueous Extract and the Alkaline Aqueous Fraction of Rhazya stricta against Some Fusarium Species
- PMID: 38202544
- PMCID: PMC10780319
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14010088
The Antifungal Activities of Silver Nano-Aggregates Biosynthesized from the Aqueous Extract and the Alkaline Aqueous Fraction of Rhazya stricta against Some Fusarium Species
Abstract
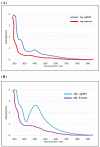
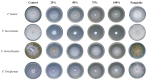
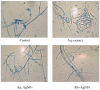
Rhazya stricta is a major medicinal species used in indigenous medicinal herbal medications in South Asia, the Middle East, Iran, and Iraq to treat a variety of ailments. The current study aimed to investigate the antifungal properties of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) made from R. stricta aqueous extract and its alkaline aqueous fraction. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), UV-vis spectrophotometry, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and transmitted electron microscopy (TEM) were used to characterize AgNPs. The produced extracts and AgNPs were tested for their antifungal efficacy against four Fusarium spp. All of the characterization experiments proved the biosynthesis of targeted AgNPs. FTIR showed a wide distribution of hydroxyl, amino, carboxyl, and alkyl functional groups among all preparations. The DLS results showed that the produced Aq-AgNPs and the Alk-AgNPs had an average size of 95.9 nm and 54.04 nm, respectively. On the other hand, TEM results showed that the Aq-AgNPs and Alk-AgNPs had average diameters ranging from 21 to 90 nm and 7.25 to 25.32 nm. Both AgNPs absorbed UV light on average at 405 nm and 415 nm, respectively. Regarding the fungicidal activity, the highest doses of Aq-extract and Aq-AgNPs inhibited the mycelial growth of F. incarnatum (19.8%, 87.5%), F. solani (28.1%, 72.3%), F. proliferatum (37.5%, 75%), and F. verticillioides (27.1%, 62.5%), respectively (p < 0.001). Interestingly, the Alk-fraction had stronger inhibition than the biosynthesized AgNPs, which resulted in complete inhibition at the doses of 10% and 20% (p < 0.001). Furthermore, microscopic analysis demonstrated that both AgNPs caused obvious morphological alterations in the treated organisms when compared to the control. In conclusion, R. stricta's Aq-extract, alkaline fraction, and their biosynthesized AgNPs show substantial antifungal efficacy against several Fusarium spp. It is the first study to highlight the prospective biological activities of R. stricta Aq-extract and its alkaline fraction against F. incarnatum, F. proliferatum, and F. verticillioides. In addition, it is the first opportunity to deeply investigate the ultrastructural changes induced in the Fusarium species treated with R. stricta crude Aq-extract and its biosynthesized AgNPs. More studies are required to investigate their biological effect against other Fusarium or fungal species.
Keywords: DLS; FTIR; Fusarium spp.; Rhazya stricta; TEM; UV-vis; antifungal activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Silver nanoparticles improve the fungicidal properties of Rhazya stricta decne aqueous extract against plant pathogens.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 14;14(1):1297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51855-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38221517 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of antifungal activity of Rhazya stricta ethanolic extracts and biogenic silver nanoparticles against pathogenic fungi.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82015-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730698 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Malva parviflora and their antifungal activity.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Apr;28(4):2229-2235. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.012. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33935565 Free PMC article.
-
The Antimicrobial Activities of Silver Nanoparticles from Aqueous Extract of Grape Seeds against Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi.Molecules. 2021 Oct 8;26(19):6081. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196081. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641623 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of antifungal activity of two preparations of green silver nanoparticles from Portulaca oleracea extract.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):2772-2781. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.12.056. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35531187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Rahman A., Almalki M. Growth and metabolic responses of Rhazya stricta Decne to habitat diversity in Makkah region, Saudi Arabia. Egypt. J. Bot. 2018;58:157–170. doi: 10.21608/ejbo.2018.1970.1133. - DOI
-
- Hajrah N.H., Abdul W.M., Abdul-Hameed Z.H., Alarif W.M., Al-Abbas N.S.A., Ayyad S.N., Omer A.M.S., Mutawakil M.Z., Hall N., Obaid A.Y., et al. Gene Expression Profiling to delineate the anticancer potential of a new alkaloid isopicrinine from Rhazya stricta. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2020;19:1534735420920711. doi: 10.1177/1534735420920711. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

