1-Hydroxyalkylphosphonium Salts-Synthesis and Properties
- PMID: 38202601
- PMCID: PMC10780258
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010018
1-Hydroxyalkylphosphonium Salts-Synthesis and Properties
Abstract
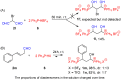
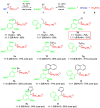
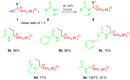
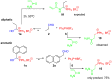
An efficient and convenient method for the synthesis of 1-hydroxyalkylphosphonium salts is described. Reactions were carried out at room temperature, in a short time, and without chromatography for product isolation. The properties of the obtained phosphonium salts were examined and discussed. In this paper, primary attention was paid to the stability of phosphonium salts, depending on the structure of the aldehydes used as substrates in their preparation. Other conditions such as the type of solvent, temperature, and molar ratio of the substrates were also investigated. Finally, the high reactivity of 1-hydroxyalkylphosphonium salts was demonstrated in reactions with amide-type substrates and (hetero)aromatic compounds. The developed step-by-step procedure (with the isolation of 1-hydroxyphosphonium salts) was compared to the one-pot protocol (in situ formation of such phosphonium salts).
Keywords: alkylating agent; alkylation; phosphonium salts; stability; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Maryanoff B.E., Reitz A.B. The Wittig olefination reaction and modifications involving phosphoryl-stabilized carbanions. Stereochemistry, mechanism, and selected synthetic aspects. Chem. Rev. 1989;89:863–927. doi: 10.1021/cr00094a007. - DOI
-
- Johnson A.W. Ylides and Imines of Phosphorus. A Wiley-Interscience Publication; New York, NY, USA: 1993. pp. 221–300.
-
- Kolodiazhnyi O.I. Phosphorus Ylides. Wiley; Weinheim, Germany: 1999. pp. 359–539.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

