A Review of Distribution and Profiles of HBCD in Different Environmental Media of China
- PMID: 38202620
- PMCID: PMC10779568
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010036
A Review of Distribution and Profiles of HBCD in Different Environmental Media of China
Abstract
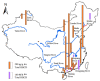
Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) is the most important flame retardant that has been used in Expanded Polystyrene foam and Extruded Polystyrene foam in the past forty years across the world. China was the major producer and user of HBCD, and the total HBCD production was about 0.3 million tons. Although HBCD was completely banned in China in 2021 because of its long-range transport, bioaccumulation and toxicity, there is still a lot of residue in the environment. Therefore, we reviewed multiple studies concerning the distribution of HBCD in diverse environmental matrices, such as in the air, dust, soil, water, sediment, and biota. Results revealed that HBCD levels in different environments in China present geographical variation and were at a high level compared with other countries. In all environmental media, relatively high HBCD concentrations have been found in industrial and urban areas. Industrialization and urbanization are two important factors that influence the concentration and distribution of HBCD in the environment. In terms of isomer, γ-HBCD was the dominant isomer in soil, water, and sediment, while in the biota α-HBCD was the predominant isomer.
Keywords: HBCD; environmental media; occurrence and distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transport of Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) into the soil, water and sediment from a large producer in China.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Jan 1;610-611:94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.039. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 28803206
-
An overview of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDs) in environmental media with focus on their potential risk and management in China.Environ Pollut. 2018 May;236:283-295. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.040. Environ Pollut. 2018. PMID: 29414350 Review.
-
Hexabromocyclododecane: concentrations and isomer profiles from sources to environmental sinks.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Dec;25(36):36624-36635. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3381-4. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30377961
-
The environmental occurrence of hexabromocyclododecane in Sweden.Chemosphere. 2004 Jan;54(1):9-21. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00758-6. Chemosphere. 2004. PMID: 14559253
-
Brominated flame retardants in the Arctic environment--trends and new candidates.Sci Total Environ. 2010 Jul 1;408(15):2885-918. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.037. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Sci Total Environ. 2010. PMID: 19815253 Review.
References
-
- Drage D.S., Heffernan A.L., Cunningham T.K., Aylward L.L., Mueller J.F., Sathyapalan T., Atkin S.L. Serum measures of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in reproductive-aged women in the United Kingdom. Environ. Res. 2019;177:108631. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108631. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

