Eco-Conscious Approach to Thermoresponsive Star-Comb and Mikto-Arm Polymers via Enzymatically Assisted Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Followed by Ring-Opening Polymerization
- PMID: 38202638
- PMCID: PMC10779862
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010055
Eco-Conscious Approach to Thermoresponsive Star-Comb and Mikto-Arm Polymers via Enzymatically Assisted Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Followed by Ring-Opening Polymerization
Abstract
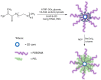
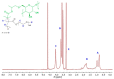
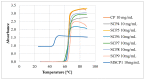
This study explores the synthesis, characterization, and application of a heterofunctional initiator derived from 2-hydroxypropyl cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD), having eight bromoester groups and thirteen hydroxyl groups allowing the synthesis of mikto-arm star-shaped polymers. The bromoesterification of HP-β-CD was achieved using α-bromoisobutyryl bromide as the acylation reagent, modifying the cyclodextrin (CD) molecule as confirmed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy analysis, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermograms. The initiator's effectiveness was further demonstrated by obtaining star-comb and mikto-arm polymers via an enzymatically assisted atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) method and subsequent ring-opening polymerization (ROP). The ATR polymerization quality and control depended on the type of monomer and was optimized by the way of introducing the initiator into the reaction mixture. In the case of ATRP, high conversion rates for poly(ethylene oxide) methyl ether methacrylate (OEOMA), with molecular weights (Mn) of 500 g/mol and 300 g/mol, were achieved. The molecular weight distribution of the obtained polymers remained in the range of 1.23-1.75. The obtained star-comb polymers were characterized by different arm lengths. Unreacted hydroxyl groups in the core of exemplary star-comb polymers were utilized in the ROP of ε-caprolactone (CL) to obtain a hydrophilic mikto-arm polymer. Cloud point temperature (TCP) values of the synthesized polymers increased with arm length, indicating the polymers' reduced hydrophobicity and enhanced solvation by water. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis revealed the ability of the star-comb polymers to create fractals. The study elucidates advancements in the synthesis and utilization of hydrophilic sugar-based initiators for enzymatically assisted ATRP in an aqueous solution for obtaining complex star-comb polymers in a controlled manner.
Keywords: ATRP; enzymes; star-comb polymers; stimuli-responsive polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
An arm-first approach to cleavable mikto-arm star polymers by RAFT polymerization.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014 Apr;35(8):840-5. doi: 10.1002/marc.201300879. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014. PMID: 24504709
-
One-Step Immobilization of Initiators for Surface-Initiated Ring Opening Polymerization and Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization by Poly(norepinephrine) Coating.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015 Feb;15(2):1597-600. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2015.9284. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26353697
-
Synthesis of Poly(ε-caprolactone)-Based Miktoarm Star Copolymers through ROP, SA ATRC, and ATRP.Polymers (Basel). 2018 Aug 2;10(8):858. doi: 10.3390/polym10080858. Polymers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30960783 Free PMC article.
-
"Polymeromics": Mass spectrometry based strategies in polymer science toward complete sequencing approaches: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2014 Jan 15;808:56-69. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.027. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Anal Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24370093 Review.
-
Latest Advances on the Synthesis of Linear ABC-Type Triblock Terpolymers and Star-Shaped Polymers by RAFT Polymerization.Polymers (Basel). 2021 May 22;13(11):1698. doi: 10.3390/polym13111698. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Open-aired synthesis of star-shaped poly[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl trimethylammonium chloride].RSC Adv. 2025 Mar 10;15(10):7649-7655. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00674k. eCollection 2025 Mar 6. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40065815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng G., Pan C. Reversible addition-fragmentation transfer polymerization in nanosized micelles formed in situ. Macromolecules. 2006;39:95–102. doi: 10.1021/ma0517897. - DOI
-
- Dadashi-Silab S., Lee I.H., Anastasaki A., Lorandi F., Narupai B., Dolinski N.D., Allegrezza M.L., Fantin M., Konkolewicz D., Hawker C.J., et al. Investigating Temporal Control in Photoinduced Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Macromolecules. 2020;53:5280–5288. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00888. - DOI
-
- Konkolewicz D., Magenau A.J.D., Averick S.E., Simakova A., He H., Matyjaszewski K. ICAR ATRP with ppm Cu catalyst in water. Macromolecules. 2012;45:4461–4468. doi: 10.1021/ma300887r. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

