A Comprehensive Review of the Classification, Sources, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Norditerpenes
- PMID: 38202643
- PMCID: PMC10780140
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010060
A Comprehensive Review of the Classification, Sources, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Norditerpenes
Abstract
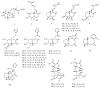
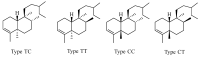
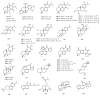
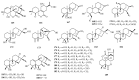
Norditerpenes are considered to be a common and widely studied class of bioactive compounds in plants, exhibiting a wide array of complex and diverse structural types and originating from various sources. Based on the number of carbons, norditerpenes can be categorized into C19, C18, C17, and C16 compounds. Up to now, 557 norditerpenes and their derivatives have been found in studies published between 2010 and 2023, distributed in 51 families and 132 species, with the largest number in Lamiaceae, Euphorbiaceae, and Cephalotaxaceae. These norditerpenes display versatile biological activities, including anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, as well as inhibitory effects against HIV and α-glucosidase, and can be considered as an important source of treatment for a variety of diseases that had a high commercial value. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the plant sources, chemical structures, and biological activities of norditerpenes derived from natural sources, serving as a valuable reference for further research development and application in this field.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antimicrobial; biological activities; chemical constituents; norditerpenes; norditerpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures













Similar articles
-
Diterpenes and norditerpenes from the roots of Dorystoechas hastata.Pharmazie. 2004 Apr;59(4):301-3. Pharmazie. 2004. PMID: 15125578
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Cytotoxic Activities of Clerodane-Type Diterpenes.Molecules. 2023 Jun 13;28(12):4744. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124744. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subtribe Hyptidinae (Lamiaceae): A promising source of bioactive metabolites.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 10;264:113225. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113225. Epub 2020 Aug 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32763419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diterpenes of Scutellaria spp.: Phytochemistry and pharmacology.Phytochemistry. 2022 Sep;201:113285. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113285. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Phytochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35728674 Review.
-
Bioactive Diterpenes, Norditerpenes, and Sesquiterpenes from a Formosan Soft Coral Cespitularia sp.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 1;14(12):1252. doi: 10.3390/ph14121252. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959653 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chemical Changes Under Heat Stress and Identification of Dendrillolactone, a New Diterpene Derivative with a Rare Rearranged Spongiane Skeleton from the Antarctic Marine Sponge Dendrilla antarctica.Mar Drugs. 2024 Dec 28;23(1):10. doi: 10.3390/md23010010. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39852512 Free PMC article.
-
Bioavailability for the Improved Therapeutic Profile of trans-Dehydrocrotonin Incorporated into a Copaiba Oil Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System: Formulation, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Antioxidant In Vitro Effect.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 8;26(10):4469. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104469. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bian X.Q., Bai J., Hu X.L., Wu X., Xue C.M., Han A.H., Su G.Y., Hua H.M., Pei Y.H. Penioxalicin, a novel 3-nor-2,3-seco-labdane type diterpene from the fungus Penicillium oxalicum TW01-1. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015;56:5013–5016. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.07.014. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

