The Promoting Role of HK II in Tumor Development and the Research Progress of Its Inhibitors
- PMID: 38202657
- PMCID: PMC10779805
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010075
The Promoting Role of HK II in Tumor Development and the Research Progress of Its Inhibitors
Abstract
Increased glycolysis is a key characteristic of malignant cells that contributes to their high proliferation rates and ability to develop drug resistance. The glycolysis rate-limiting enzyme hexokinase II (HK II) is overexpressed in most tumor cells and significantly affects tumor development. This paper examines the structure of HK II and the specific biological factors that influence its role in tumor development, as well as the potential of HK II inhibitors in antitumor therapy. Furthermore, we identify and discuss the inhibitors of HK II that have been reported in the literature.
Keywords: Warburg effect; antitumor; glycolysis; hexokinase II; inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
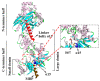
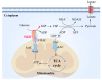
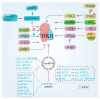
 , cicroRNA;
, cicroRNA;  , miRNA;
, miRNA;  , phosphorylation;
, phosphorylation;  , ubiquitination;
, ubiquitination;  , active.
, active.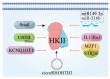
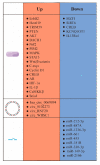
 , protein;
, protein;  , cicro RNA;
, cicro RNA;  , miRNA.
, miRNA.
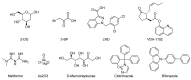
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of novel methyl jasmonate derivatives and evaluation of their biological activity in various cancer cell lines.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Oct;91:103146. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103146. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31377389
-
Virtual Screening and Biological Activity Evaluation of New Potent Inhibitors Targeting Hexokinase-II.Molecules. 2022 Nov 4;27(21):7555. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217555. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364382 Free PMC article.
-
Warburg effect, hexokinase-II, and radioresistance of laryngeal carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):14133-14146. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13044. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27823965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chrysin inhibited tumor glycolysis and induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hexokinase-2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Mar 20;36(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0514-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28320429 Free PMC article.
-
GLUT and HK: Two primary and essential key players in tumor glycolysis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2024 May;100:17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2024.03.001. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Semin Cancer Biol. 2024. PMID: 38494080 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: dedicator to maintain tumor homeostasis.Hum Cell. 2024 Nov 28;38(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01154-y. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 39607530 Review.
-
Glucose Metabolism and Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 22;26(5):1879. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051879. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic inhibitory effect of atmospheric pressure plasma and berberine on non‑small cell lung cancer cells via inducing apoptosis.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 7;52(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10132-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39643828
-
An in- vitro measurement for the toxicity of peptides inhibit hexokinase II in breast cancer cell lines.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 27;15(1):10660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94858-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40148397 Free PMC article.
-
Potent Biological Activity of Fluorinated Derivatives of 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose in a Glioblastoma Model.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 1;12(10):2240. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102240. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng R.S., Zhang S.W., Sun K.X., Chen R., Wang S.M., Li L., Zeng H.M., Wei W.W., He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2016. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023;45:212–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

