Discovery of a 4-Hydroxy-3'-Trifluoromethoxy-Substituted Resveratrol Derivative as an Anti-Aging Agent
- PMID: 38202669
- PMCID: PMC10779923
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010086
Discovery of a 4-Hydroxy-3'-Trifluoromethoxy-Substituted Resveratrol Derivative as an Anti-Aging Agent
Abstract
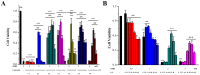
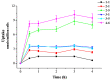
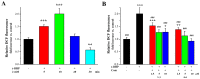
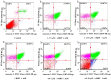
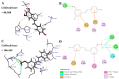
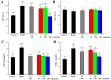
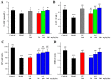
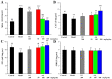
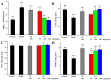
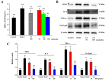
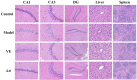
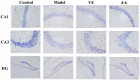
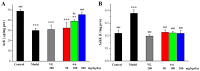
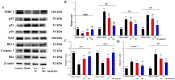
With the intensification of population aging, aging-related diseases are attracting more and more attention, thus, the study of aging mechanisms and anti-aging drugs is becoming increasingly urgent. Resveratrol is a potential candidate as an anti-aging agent, but its low bioavailability limits its application in vivo. In this work, a 4-hydroxy-3'-trifluoromethoxy-substituted resveratrol derivative (4-6), owing to its superior cell accumulation, could inhibit NO production in an inflammatory cell model, inhibit oxidative cytotoxicity, and reduce ROS accumulation and the population of apoptotic cells in an oxidative stress cell model. In D-galactose (D-gal)-stimulated aging mice, 4-6 could reverse liver and kidney damage; protect the serum, brain, and liver against oxidative stress; and increase the body's immunity in the spleen. Further D-gal-induced brain aging studies showed that 4-6 could improve the pathological changes in the hippocampus and the dysfunction of the cholinergic system. Moreover, protein expression related to aging, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in the brain tissue homogenate measured via Western blotting also showed that 4-6 could ameliorate brain aging by protecting against oxidative stress and reducing apoptosis. This work revealed that meta-trifluoromethoxy substituted 4-6 deserved to be further investigated as an effective anti-aging candidate drug.
Keywords: D-galactose; anti-aging; apoptosis; inflammation; oxidative stress; resveratrol derivatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COP-22 Alleviates D-Galactose-Induced Brain Aging by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6708-6720. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03976-1. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38347285 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effect of PL 1-3 on D-galactose-induced aging mice.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1304801. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1304801. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38235117 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effect of supercritical fluid extract of Chrysanthemum indicum Linnén against D-galactose induced brain and liver injury in senescent mice via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Apr 24;234:44-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.12.050. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30610932
-
Polydatin attenuates d-galactose-induced liver and brain damage through its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in mice.Food Funct. 2016 Nov 9;7(11):4545-4555. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01057a. Food Funct. 2016. PMID: 27714005
-
Systemic and renal oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hypertension: modulation of long-term control of arterial blood pressure by resveratrol.Front Physiol. 2014 Aug 5;5:292. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00292. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25140155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut-Brain Axis-Based Polygala Tenuifolia and Magnolia Officinalis Improve D-gal-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice Through cAMP and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Mar 13;19:1869-1894. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S506545. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40098911 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Application of Resveratrol and Its Derivatives in Central Nervous System Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13338. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413338. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Resveratrol Derivatives: Structural Modifications and Biological Activities.Molecules. 2025 Feb 19;30(4):958. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040958. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

