Therapeutic Potential of Curcumin, a Bioactive Compound of Turmeric, in Prevention of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes through the Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
- PMID: 38202711
- PMCID: PMC10779985
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010128
Therapeutic Potential of Curcumin, a Bioactive Compound of Turmeric, in Prevention of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes through the Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
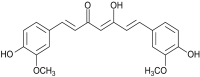
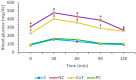
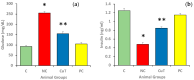
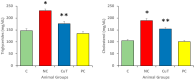
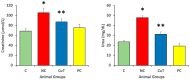
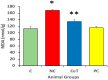
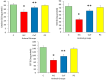
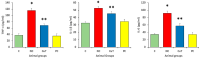
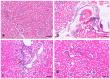
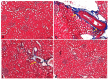
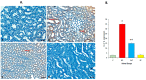
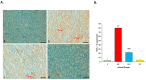
This study evaluates the anti-diabetic potential and underlying mechanisms of curcumin in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats. The rats were randomly divided into four groups: normal control, negative control (diabetic group), diabetic group receiving glibenclamide (positive control group), and curcumin plus STZ (treatment group). The anti-diabetic activities of curcumin were examined at a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight through physiological, biochemical, and histopathological analysis. Compared to the normal control group rats, elevated levels of glucose, creatinine, urea, triglycerides (TG), and total cholesterol (TC) and low levels of insulin were found in the negative control rats. Curcumin treatment showed a significant decrease in these parameters and an increase in insulin level as compared to negative control rats. In negative control rats, a reduced level of antioxidant enzymes and an increased level of lipid peroxidation and inflammatory marker levels were noticed. Oral administration of curcumin significantly ameliorated such changes. From histopathological findings, it was noted that diabetic rats showed changes in the kidney tissue architecture, including the infiltration of inflammatory cells, congestion, and fibrosis, while oral administration of curcumin significantly reduced these changes. Expression of IL-6 and TNF-α protein was high in diabetic rats as compared to the curcumin treatment groups. Hence, based on biochemical and histopathological findings, this study delivers a scientific suggestion that curcumin could be a suitable remedy in the management of diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: curcumin; diabetes mellitus; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Curcumin, the active principle of turmeric (Curcuma longa), ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 Oct;33(10):940-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04468.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17002671
-
Effect of turmeric and curcumin on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat.Med Sci Monit. 2007 Dec;13(12):BR286-92. Med Sci Monit. 2007. PMID: 18049430
-
Curcumin and turmeric delay streptozotocin-induced diabetic cataract in rats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Jun;46(6):2092-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-1304. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15914628
-
Curcumin Attenuates Testicular Injury in Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jul 31;2018:7468019. doi: 10.1155/2018/7468019. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30151389 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of curcumin, a bioactive component of turmeric, on type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications: an updated review.Food Funct. 2022 Nov 28;13(23):11999-12010. doi: 10.1039/d2fo02625b. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 36367124 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Behind Organ-Related Aging and Regulatory Effects of Natural Therapeutics.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01792-5. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40528054 Review.
-
Unlocking the Pharmacological Potential of Myricetin Against Various Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 28;26(9):4188. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094188. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the role of curcumin in mitigating oxidative stress to alleviate lipid metabolism disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;16:1517174. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1517174. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39950117 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

