Bio-Guided Assay of Ephedra foeminea Forssk Extracts and Anticancer Activities: In Vivo, In Vitro, and In Silico Evaluations
- PMID: 38202783
- PMCID: PMC10780881
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010199
Bio-Guided Assay of Ephedra foeminea Forssk Extracts and Anticancer Activities: In Vivo, In Vitro, and In Silico Evaluations
Abstract
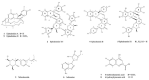
Ephedra is one of the oldest known medicinal plants and the largest genera of the Ephedraceae family. In vivo antitumor evaluation of Ephedra foeminea revealed that ethyl acetate (EtOAc) was the most bioactive fraction. Bio-guided fractionation of EtOAc fraction afforded nine compounds isolated for the first time from the plant species. Macrocyclic spermine alkaloids (1,9), proanthocyanidins (2,4,5), quinoline alkaloids (7,8), phenolic (3), and nucleoside (6) were identified and elucidated by spectroscopic analyses including 1D and 2D NMR, ESI-MS-MS spectrometry. The tested compounds exhibited moderate anticancer activity, except for the kynurenic acid derivative (6-mKYNA) which showed significant cytotoxicity and remarkable inhibition of CA-19.9 and CA-125 tumor biomarkers. In-silico study was conducted to determine the anti-proliferative mechanism of 6-mKYNA by using the CK2 enzyme active site. Moreover, the ADME computational study suggested that 6-mKYNA is an effective candidate with a promising pharmacokinetic profile and therapeutic potential against various types of cancer.
Keywords: 6-methoxykynurenic acid; ADME; Ephedra foeminea; alkaloids; in silico; proanthocyanidins; tumor marker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Potential Anticancer Activity of Crude Ethanol, Ethyl Acetate, and Water Extracts of Ephedra foeminea on Human Osteosarcoma U2OS Cell Viability and Migration.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 9;2020:3837693. doi: 10.1155/2020/3837693. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32695811 Free PMC article.
-
Benzaldehyde is a precursor of phenylpropylamino alkaloids as revealed by targeted metabolic profiling and comparative biochemical analyses in Ephedra spp.Phytochemistry. 2012 Sep;81:71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.05.018. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Phytochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22727117
-
Protective effects of extracts from Ephedra foeminea Forssk fruits against oxidative injury in human endothelial cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:112976. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112976. Epub 2020 May 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32428657
-
Phytochemistry and pharmacology of genus Ephedra.Chin J Nat Med. 2018 Nov;16(11):811-828. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30123-7. Chin J Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 30502763 Review.
-
A Review on Worldwide Ephedra History and Story: From Fossils to Natural Products Mass Spectroscopy Characterization and Biopharmacotherapy Potential.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Apr 30;2020:1540638. doi: 10.1155/2020/1540638. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32419789 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Medicinal effects of Ephedra foeminea aqueous extracts: Metabolomic characterization, biological evaluation, and molecular docking.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 24;20(7):e0328995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328995. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40705749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hollander L., Vander B., Baguley G. Evolution of seed dispersal in North American Ephedra. Evol. Ecol. 2010;24:333–345. doi: 10.1007/s10682-009-9309-1. - DOI
-
- González-Juárez D.E., Escobedo-Moratilla A., Flores J., Hidalgo-Figueroa S., Martínez-Tagüeña N., Pérez-Miranda S., Ramírez-Hernández A., Trujillo J. A review of the Ephedra genus: Distribution, ecology, ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties. Molecules. 2020;25:3283. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143283. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li L., Chen J. Research progress on Ephedra and its active ingredients. J. Xinjiang Med. Univ. 2003;26:606–608.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

