H2S/Butane Dual Gas Sensing Based on a Hydrothermally Synthesized MXene Ti3C2Tx/NiCo2O4 Nanocomposite
- PMID: 38202785
- PMCID: PMC10780481
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010202
H2S/Butane Dual Gas Sensing Based on a Hydrothermally Synthesized MXene Ti3C2Tx/NiCo2O4 Nanocomposite
Abstract
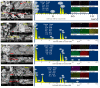
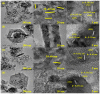
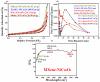
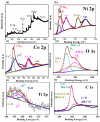
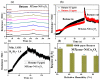
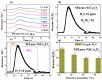
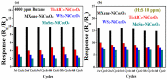
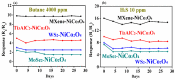
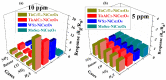
Real-time sensing of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) at room temperature is important to ensure the safety of humans and the environment. Four kinds of different nanocomposites, such as MXene Ti3C2Tx, Ti3AlC2, WS2, and MoSe2/NiCo2O4, were synthesized using the hydrothermal method in this paper. Initially, the intrinsic properties of the synthesized nanocomposites were studied using different techniques. P-type butane and H2S-sensing behaviors of nanocomposites were performed and analyzed deeply. Four sensor sheets were fabricated using a spin-coating method. The gas sensor was distinctly part of the chemiresistor class. The MXene Ti3C2Tx/NiCo2O4-based gas sensor detected the highest response (16) toward 10 ppm H2S at room temperature. In comparison, the sensor detected the highest response (9.8) toward 4000 ppm butane at 90 °C compared with the other three fabricated sensors (Ti3AlC2, WS2, and MoSe2/NiCo2O4). The MXene Ti3C2Tx/NiCo2O4 sensor showed excellent responses, minimum limits of detection (0.1 ppm H2S and 5 ppm butane), long-term stability, and good reproducibility compared with the other fabricated sensors. The highest sensing properties toward H2S and butane were accredited to p-p heterojunctions, higher BET surface areas, increased oxygen species, etc. These simply synthesized nanocomposites and fabricated sensors present a novel method for tracing H2S and butane at the lowest concentration to prevent different gas-exposure-related diseases.
Keywords: MXene Ti3C2Tx; butane sensing; ppb-level H2S-sensing; sensor sheets; spherical NiCo2O4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Kaur M., Dadhich B.K., Singh R., Bagwaiya T., Bhattacharya S., Debnath A., Muthe K.P., Gadkari S.C. RF sputtered SnO2: NiO thin films as sub-ppm H2S sensor operable at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017;242:389–403. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.054. - DOI
-
- Lee K.Y., Hsieh J.C., Chen C.A., Chen W.L., Meng H.F., Lu C.J., Horng S.F., Zan H.W. Ultrasensitive detection of hydrogen sulfide gas based on perovskite vertical channel chemo-sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021;326:128988. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128988. - DOI
-
- Fan H.T., Zeng Y., Xu X.J., Lv N., Zhang T. Hydrothermal synthesis of hollow ZnSnO3 microspheres and sensing properties toward butane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011;153:170–175. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.10.026. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

