Paeonol Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Senescence via SIRT1/P53/TRF2 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38202844
- PMCID: PMC10780795
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010261
Paeonol Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Senescence via SIRT1/P53/TRF2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
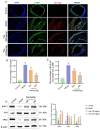
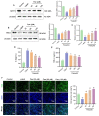
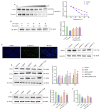
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease leading to various vascular diseases. Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) senescence promotes atherosclerotic inflammation and the formation of plaque necrosis core, in part through telomere damage mediated by a high-fat diet. Our previous research found that paeonol, a potential anti-inflammatory agent extracted from Cortex Moutan, could significantly improve VSMCs dysfunction. However, the impact of paeonol on the senescence of VSMCs remains unexplored. This study presents the protective effects of paeonol on VSMCs senescence, and its potential activity in inhibiting the progression of atherosclerosis in vivo and in vitro. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is a nuclear deacetylase involved in cell proliferation, senescence, telomere damage, and inflammation. Here, SIRT1 was identified as a potential target of paeonol having anti-senescence and anti-atherosclerosis activity. Mechanistic studies revealed that paeonol binds directly to SIRT1 and then activates the SIRT1/P53/TRF2 pathway to inhibit VSMCs senescence. Our results suggested that SIRT1-mediated VSMCs senescence is a promising druggable target for atherosclerosis, and that pharmacological modulation of the SIRT1/P53/TRF2 signaling pathway by paeonol is of potential benefit for patients with atherosclerosis.
Keywords: SIRT1; atherosclerosis; cell senescence; paeonol; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SIRT6 Protects Smooth Muscle Cells From Senescence and Reduces Atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 2021 Feb 19;128(4):474-491. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318353. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33353368 Free PMC article.
-
Paeonol attenuates atherosclerosis by regulating vascular smooth muscle cells apoptosis and modulating immune cells infiltration through reducing LTβR expression.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156196. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156196. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39520955
-
Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Senescence Promotes Atherosclerosis and Features of Plaque Vulnerability.Circulation. 2015 Nov 17;132(20):1909-19. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016457. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 26416809
-
Beneficial Effects Exerted by Paeonol in the Management of Atherosclerosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 7;2018:1098617. doi: 10.1155/2018/1098617. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30524649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective role of Sirt1 in vascular tissue: its relationship to vascular aging and atherosclerosis.Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Oct 15;8(10):2290-2307. doi: 10.18632/aging.101068. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 27744418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paeonol alleviates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury by targeting the heme oxygenase-1/phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):591-600. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03307-0. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39037459
-
Unraveling the AMPK-SIRT1-FOXO Pathway: The In-Depth Analysis and Breakthrough Prospects of Oxidative Stress-Induced Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;14(1):70. doi: 10.3390/antiox14010070. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Tryptanthrin by Regulating TLR4/MyD88/ROS/NF-κB, JAK/STAT3, and Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 3;9(28):30904-30918. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03795. eCollection 2024 Jul 16. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39035974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matthews C., Gorenne I., Scott S., Figg N., Kirkpatrick P., Ritchie A., Goddard M., Bennett M. Vascular smooth muscle cells undergo telomere-based senescence in human atherosclerosis: Effects of telomerase and oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2006;99:156–164. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000233315.38086.bc. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

